Digestive Enzymes Biology Diagrams Activity III: Digestive Enzymes and Factors Affecting their Function; Table 1. Several important digestive enzymes, and details about their production and activity. Activity IIIA: Effects of Time and Temperature on Starch Hydrolysis (breakdown) by Amylase; Table 2. Data from exercise on the effects of time and temperature on amylase activity. Pepsin: Pepsin is secreted by the stomach to break down proteins into peptides, or smaller groupings of amino acids.Those amino acids are then either absorbed or broken down further in the small intestine. Trypsin: Trypsin forms when an enzyme secreted by the pancreas is activated by an enzyme in the small intestine. Trypsin then activates additional pancreatic enzymes, such as It produces the most important digestive enzymes, which are those that break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Types of Digestive Enzymes. There are many digestive enzymes. The main digestive enzymes made in the pancreas include: Amylase (made in the mouth and pancreas; breaks down complex carbohydrates)
.PNG)
DIGESTIVE ENZYMES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS. The human pancreas has the largest capacity for protein synthesis of any organ in the human body. Much of the capacity is devoted to synthesis of the digestive enzymes that are secreted in the intestinal lumen. Table 1 lists the major proteolytic, amylolytic, lipolytic and nuclease digestive enzymes [64 Diagram of the digestive enzymes in the small intestine and pancreas. Digestive enzymes take part in the chemical process of digestion, which follows the mechanical process of digestion.Food consists of macromolecules of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats that need to be broken down chemically by digestive enzymes in the mouth, stomach, pancreas, and duodenum, before being able to be absorbed There are thousands of individual enzymes in the body. Each type of enzyme only has one job. For example, the enzyme sucrase breaks down a sugar called sucrose. Lactase breaks down lactose, a kind of sugar found in milk products. Some of the most common digestive enzymes are: Carbohydrase breaks down carbohydrates into sugars.

Digestive Enzymes 101: Why They're Important Biology Diagrams
Digestive enzyme production also gradually declines with aging . Types of Digestive Enzymes & How They Work Fats: Lipases. Lipases are enzymes that break down fats. They are produced in the pancreas but can also be extracted from plants, animals, and fungi [40, 41, 42]: Sugars: Amylases. Some diseases directly impact digestive enzyme production, which can lead to chronic enzyme insufficiency, which is technically termed exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. The name signifies that the problem is the pancreas, which isn't producing enough enzymes to fuel the digestive processes in the small intestines. (When I looked up
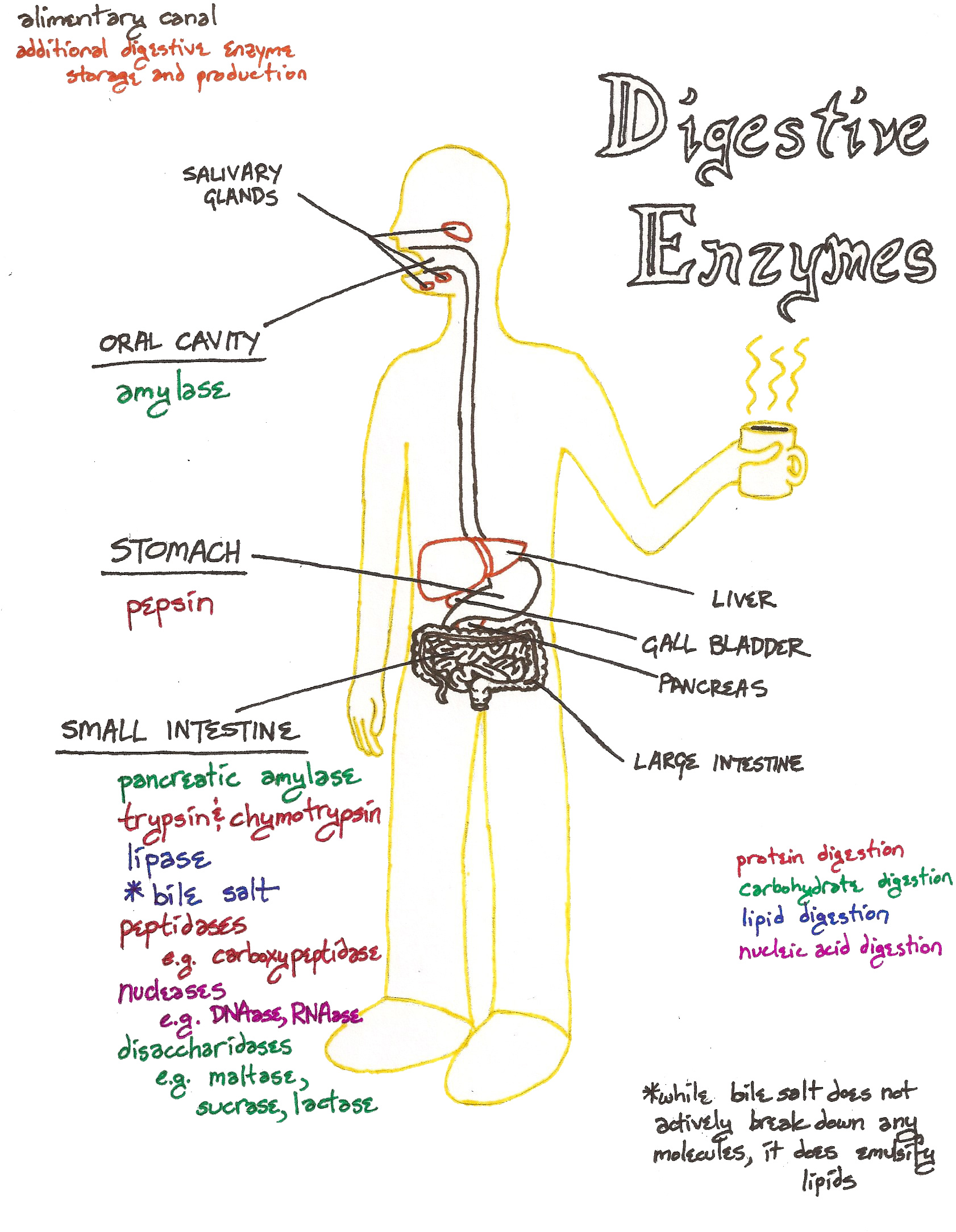
Amylase. This enzyme breaks down carbohydrates, or starches, into sugar molecules. Insufficient amylase can lead to diarrhea. Lipase. This works with liver bile to break down fats. Digestive enzymes are predominantly produced by the pancreas and there are three major types: Amylase: Enzymes that digest starches. Protease: Enzymes that digest proteins.
