Characterisation of oxidative phosphorylation in skeletal muscle Biology Diagrams Abstract. Mitochondria play an essential role in oxidative phosphorylation, fatty acid oxidation, and the regulation of apoptosis. However, this organelle also produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) that continually inflict oxidative damage on mitochondrial DNA, proteins, and lipids, which causes further production of ROS.

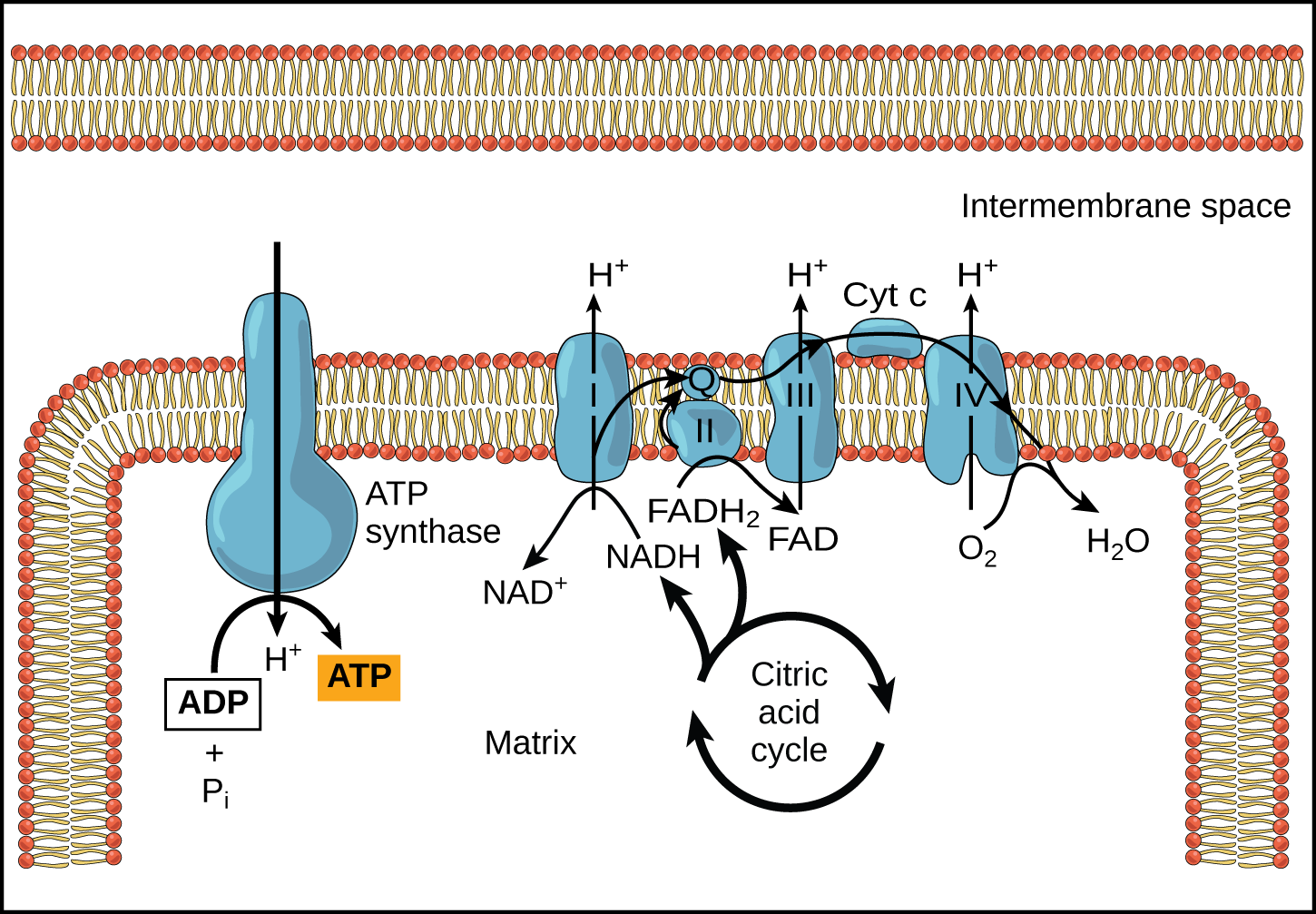
Oxidative phosphorylation is a cellular process that harnesses the reduction of oxygen to generate high-energy phosphate bonds in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is a series of oxidation-reduction reactions that involve the transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen across several protein, metal, and lipid complexes in the mitochondria known as the electron transport chain The result indicated that alisertib treated cancer cells are more sensitive to the genetic perturbation of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Mechanistic investigation indicated that alisertib treatment, as well as other mitotic kinase inhibitors, rapidly reduces the intracellular ATP level to generate a status that is highly addictive to Sustained cellular function and viability of high-energy demanding post-mitotic cells rely on the continuous supply of ATP. The utilization of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation for efficient

Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation Regulates the Fate ... Biology Diagrams
Mitosis is a key step in the cell cycle, and it governs the production of new daughter cells from old ones. During this process, mitotic kinases, such as CDK1, Aurora-A, Aurora-B, and PLK1, are This fact supports the role of mitochondria in biochemical requirements of highly proliferative neuronal stem cells and post-mitotic neurons. During neuronal differentiation, the number of mitochondria per cell increases, Oxidative phosphorylation in cells is not fully efficient. Decrease of the proton gradient across the inner Distinct roles have been demonstrated for mitochondrial fission and fusion in different cancer contexts. Targeting of factors mediating mitochondrial dynamics may be directly related to impairment of oxidative phosphorylation, which is essential to sustain cancer cell growth and can also alter sensitivity to chemotherapeutic compounds.
Shin et al. report that ATP-linked mitochondrial respiration controls the Th17 and Treg cell fate decision by supporting TCR signaling and Th17-associated molecular events. Inhibition of mitochondrial OXPHOS ablates Th17 pathogenicity in a mouse model of MS and results in generation of functionally suppressive Treg cells under Th17 conditions. Oxidative stress is known to induce cell cycle arrest, but the effects of ROS on the cell cycle, especially mitotic progression, are not fully understood. Cdc25C, a phosphatase that removes inhibitory phosphorylation from Cyclin B/Cdk1, is sensitive to oxidation.
