Where are ganglia of the parasympathetic division located Biology Diagrams There are three ganglia within this chain that are of interest - the superior, middle and inferior cervical ganglia. The sympathetic fibres synapse with these ganglia, with post ganglionic branches continuing into the head and neck. Each of the three ganglia are related to specific arteries in the head and neck. The sympathetic nervous system is comprised exclusively of efferent neurons and divides into the left and right sympathetic chains.[1] Each sympathetic chain extends from the skull base to the coccyx paravertebrally, carrying preganglionic fibers from the spinal cord that synapse in an adjacent ganglion, from which ascending and descending postganglionic fibers head toward viscera.[2][3] The
Pass through the sympathetic trunk ganglion without synapsing, form splanchnic nerves and reach one of the collateral sympathetic ganglion in abdomen such as coeliac or superior mesenteric ganglion. Postganglionic fibers from the parasympathetic ganglia in head & neck reach the salivary and lacrimal glands , intraocular muscles via branches

14.2G: Sympathetic Nervous System Biology Diagrams
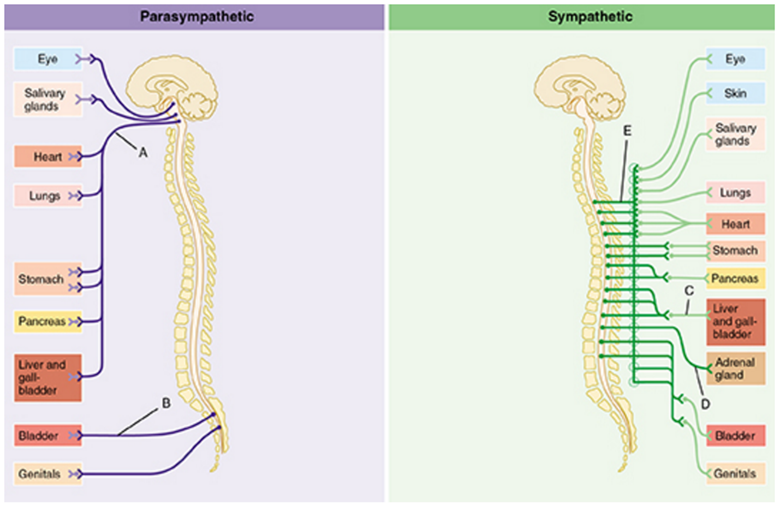
Key Terms. paravertebral ganglia: Located along the length of the sympathetic trunk, these ganglia are designated as cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral and, except in the neck, closely correspond in number to the vertebrae.; fight or flight: All the coordinated physiological responses that the sympathetic nervous system initiates in response to stress or other emergency situations. The sympathetic ganglia, or paravertebral ganglia, are autonomic ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system.Ganglia are 20,000 to 30,000 afferent and efferent nerve cell bodies that run along on either side of the spinal cord.Afferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the body to the brain and spinal cord, while efferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the brain and spinal cord The sympathetic trunk is a fundamental part of the sympathetic nervous system, and part of the autonomic nervous system. It allows nerve fibres to travel to spinal nerves that are superior and inferior to the one in which they originated. Also, a number of nerves, such as most of the splanchnic nerves, arise directly from the trunks.

The sympathetic nervous system (SNS), mediated by the sympathetic chain (trunk) and ganglia, is a major division of the autonomic nervous system.It is composed of general visceral afferent and efferent axons that allow for involuntary control of bodily functions via the hypothalamus.. The overarching function of the sympathetic system is to control the 'fight, fright or flight

Structure, Function, Location, Diagram Biology Diagrams
The sympathetic trunk is a paired structure of nerve fibers that runs along both sides of the vertebral column. It is a key part of the autonomic nervous system, specifically the sympathetic division, and extends from the base of the skull down to the coccyx. The trunk consists of a chain of interconnected sympathetic ganglia that are located lateral to the vertebral bodies.
