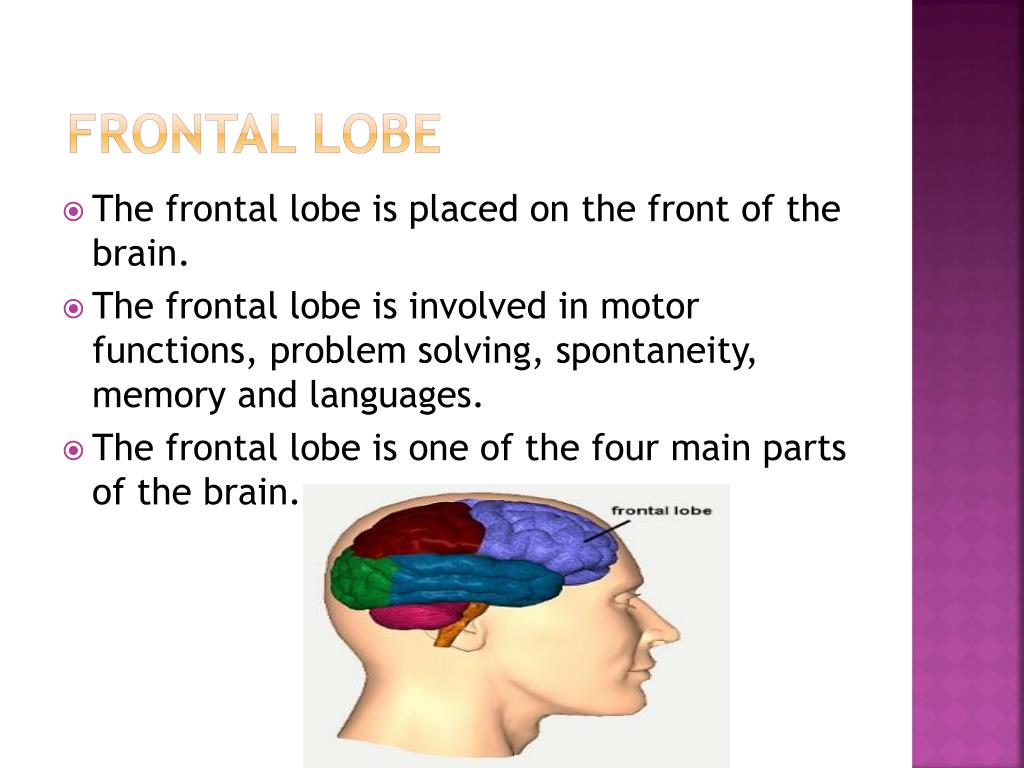
Understanding the Frontal Lobe Functions Structure and Impact on Health Biology Diagrams The frontal lobe is a large part of the brain that helps humans perform complex tasks, innovate, and imagine. Damage to the frontal lobe can cause a range of symptoms, such as behavioral problems, depression, and weakness on one side of the body. The frontal lobe is a vital part of the brain that controls speech, memory, personality, and more. Learn about its location, roles, and how damage can affect it. Learn about the frontal lobe, the forward-most part of your brain that controls many abilities, such as reasoning, social understanding, executive functions and voluntary movements. Find out what conditions and disorders can affect the frontal lobe and how to keep it healthy.
Learn about the frontal lobe, the largest part of your brain that controls motor tasks, judgment, social understanding, and more. Find out how the frontal lobe develops, what disorders can affect it, and how to keep it healthy.

Frontal Lobe Function, Location in Brain, Damage, More Biology Diagrams
The Frontal Lobe's Fantastic Functions: More Than Just a Pretty Face. Now that we've got a handle on the frontal lobe's structure, let's dive into its functions. Buckle up, folks - this is where things get really interesting! First up on our tour of frontal lobe functions is the star of the show: executive functions. and how lesions of the frontal lobes may present symptomatically within each functional area, and conclude with an overview of neuropsychological assessment for frontal lobe functions. Fig. 10.2 Mesial view of the frontal lobe including primary motor, supplementary motor, micturation center, and prefrontal cortex/anterior cingulate Learn about the frontal lobe, the largest lobe of the brain, located in the anterior aspect of the cranial cavity. It is involved in higher cognitive functions, such as decision making, planning, speech production and voluntary movement.
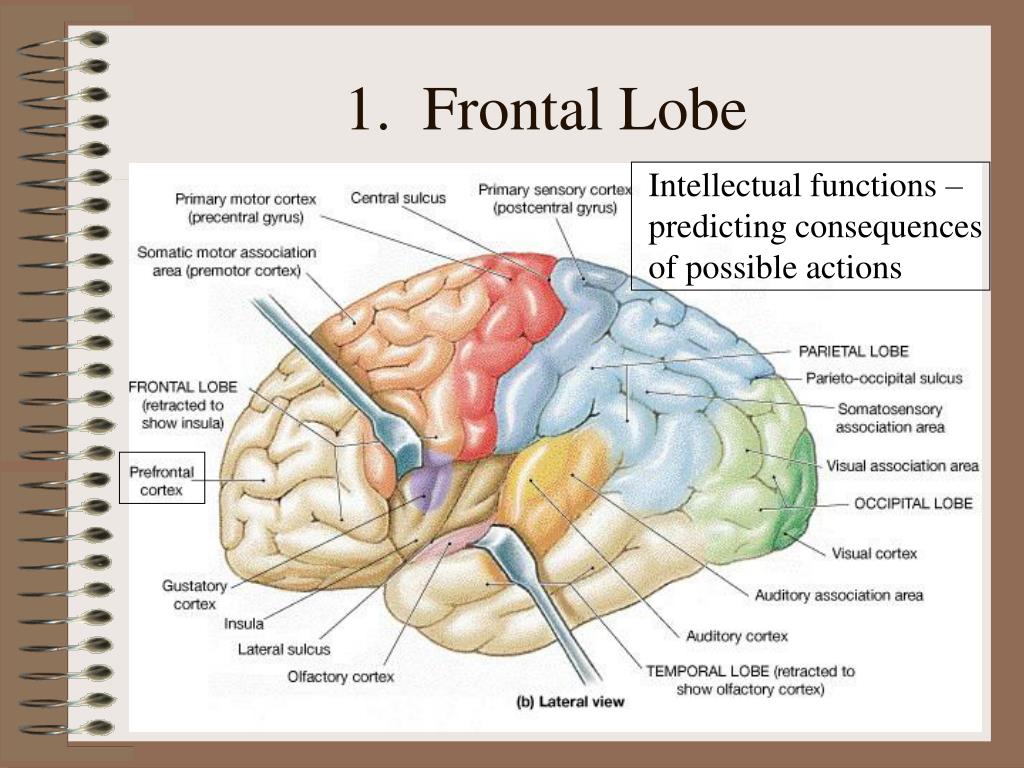
Learn about the frontal lobe, the largest and most complex part of your brain. It controls voluntary movements, speech, reasoning, planning, and impulse control. Find out what happens when it's damaged and how to treat it. The frontal lobe is the largest lobe of the brain and controls voluntary movements, speech, reasoning, and emotions. It is divided into four parts: lateral, polar, orbital, and medial, and contains the prefrontal cortex, the action cortex, and the dopaminergic pathways. The frontal lobe is the brain's largest region, involved in higher cognitive functions, such as planning, problem-solving, language, and emotion. Learn about its substructures, how damage affects them, and how to diagnose and treat the symptoms.