Tundra Food Web Diagram Biology Diagrams Seasonal Shifts in Tundra Food Webs. The tundra experiences dramatic seasonal shifts, with summer abundance and winter scarcity significantly impacting food web dynamics. These changes drive migration, hibernation, and adaptations in both plants and animals, shaping species interactions throughout the year.

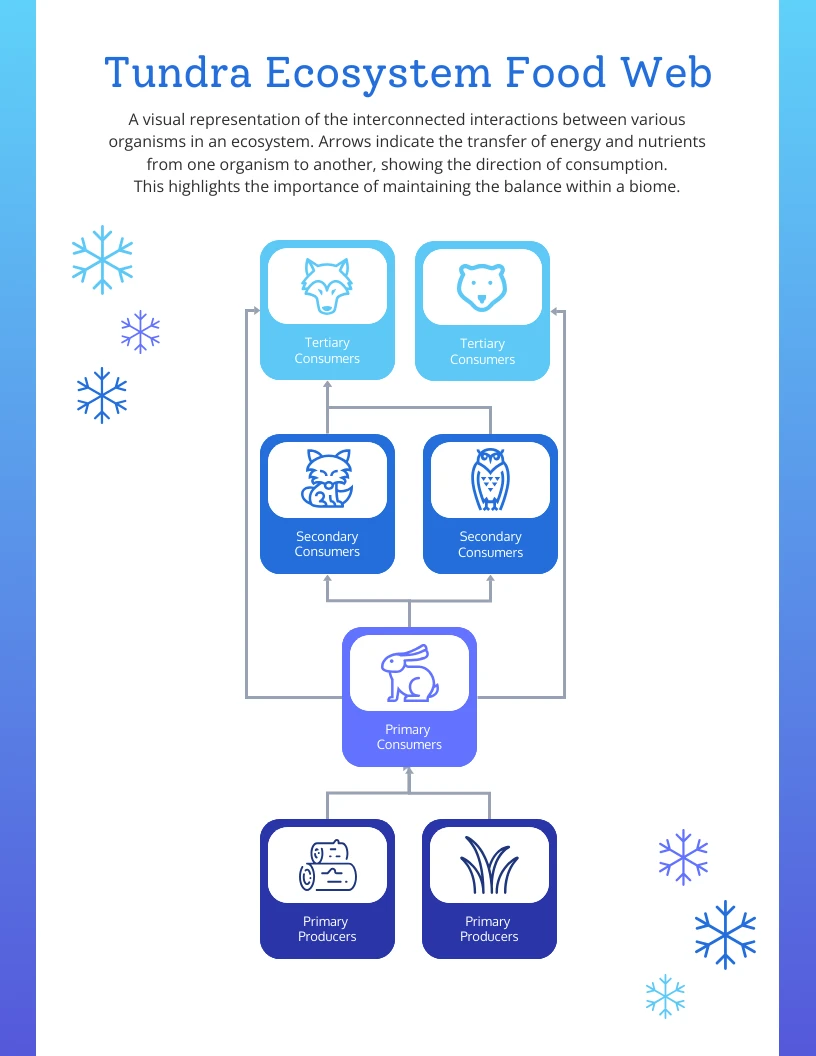
The tundra biome is characterized by a cold, dry climate. The plants and animals in tundra ecosystems form communities based on the transfer of energy between organisms. A food chain shows how energy is transferred from one living thing to another. Food chains intersect to form food webs. The fragile food chains of tundra support some of the most amazing species on the planet, including the likes of gray wolves, polar bears, snowy owls, and Arctic foxes. For tundra plants and animals, survival is not just about battling the harsh environment of this biome, but is equally about being a part of its complex food web. There are three types of tundra biome found throughout the world: As the predator-prey relationship is complex, the tundra food chain looks more like a food web than a food chain. However, due to its low biodiversity, the food chains in this biome usually have 3-4 links. Tundra Food Chain Examples# Decomposers# Producers#

The Tundra Biology Diagrams
The Siberian food chain is divided into. In Siberian tundra, the producers are lichens, grasses, and arctic wildflowers. The herbivores are arctic hare, lemming, and musk. The carnivores include hawks, polar bears, and wolves. This food web is missing the main component in the transfer of energy. 4. What are the decomposers in the tundra biome Tundra Food Web Food web and Explanation. This food web shows the cycle at which food is transferred between organisms. First, the sun helps grow the plants (through photosynthesis) to provide food for the herbivores to graze. The food web is missing a main component in the transfer of energy. After the carnivores hunt and eat their prey The specifics, however, are much more intricate and vary based on the tundra location (arctic vs. alpine). Primary Producers: The Foundation of Tundra Life. The base of any food chain is its primary producers, organisms that can create their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. In the tundra, primary producers face unique challenges.

A food chain in the tundra biome described with examples and a simple diagram. Physics. the tundra food chain looks more like a food web than a food chain. However, due to its low biodiversity, the food chains in this biome usually have 3-4 links. A Simple Explanation of the Food Chain in the Tundra Region - Sciencestruck.com; This takes the form of a tundra food web diagram that shows all connections and directions of energy flow between organisms in the ecosystem. Terrestrial Tundra. Terrestrial Tundra. Tundra food webs are relatively simplistic compared to other biomes because biodiversity is low. The top predators of the system tend to be mammalian carnivores On the bottom of the food chain in the Alpine tundra are tussock grasses, small-leafed shrubs, dwarf trees, heaths, alpine sunflowers, mosses, lichens, bristlecone pine, and a host of perennials. Plenty of animals in the middle of the food chain eat these plants. Some of the Top of the Tundra's Food Chain Predators