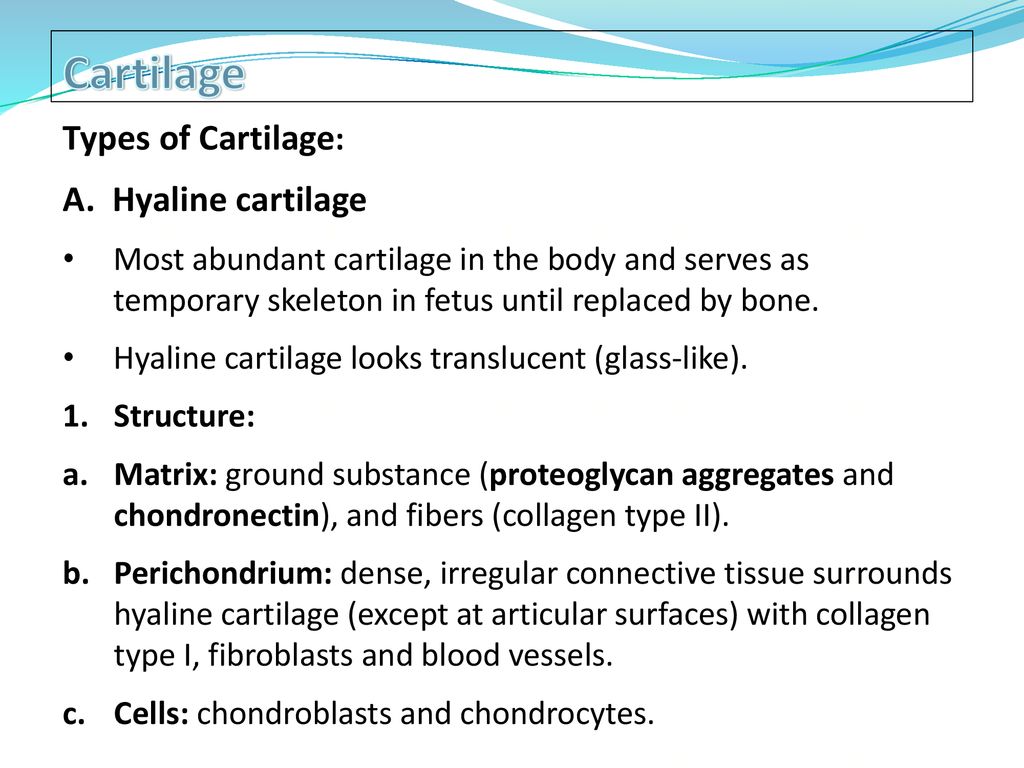
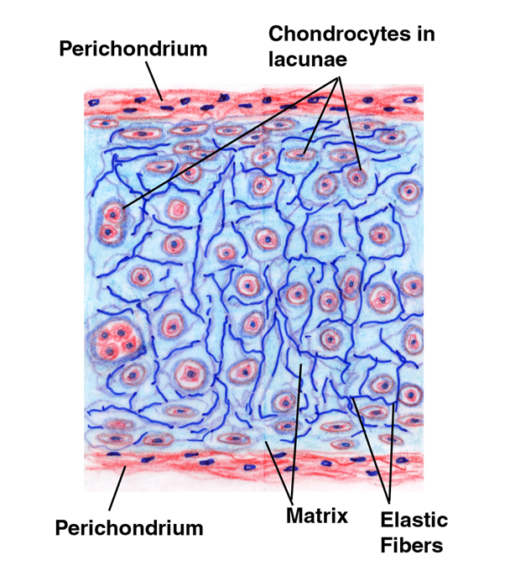
Topic 4 Cartilage and Bone Biology Diagrams Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in multiple areas of the body, including joints, the ear and nose, and intervertebral discs. Hyaline cartilage, the most abundant type of cartilage, plays a supportive role and assists in movement.. Formed by the process of chondrogenesis, the resulting chondrocytes are capable of producing large amounts of collagenous extracellular matrix and Types of cartilage. Image Source: Physiopedia. Elastic cartilage is the most flexible type of cartilage that provides support to body parts requiring bending and movement for proper function. Elastic cartilage can return to its previous shape even after enduring high pressure. Elastic cartilage is found in structures like the larynx, eustachian tubes, and external ear that require both support Key Terms. chondroitin sulfate: An important structural component of cartilage that provides much of its resistance to compression.. connective tissue: A type of tissue found in animals whose main function is to bind other tissue systems (such as muscle to skin) or organs.It consists of the following three elements: cells, fibers, and a ground substance (or extracellular matrix).
Cartilage is flexible connective tissue found throughout the whole body. It is stiffer than most other connective tissue types but flexible enough to withstand compressive forces without breaking or becoming permanently deformed. This article will discuss the function, structure and different types of cartilage, as well as its neuromuscular
TeachMePhysiology Biology Diagrams
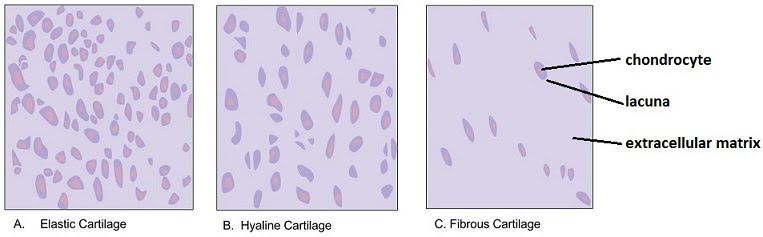
Cartilage is a semi-rigid but flexible avascular connective tissue found at various sites within the body. With a pliable structure composed primarily of water, this tissue type is also extremely tough. Cartilage is found throughout the human body in areas such as the joints, nose, airway, intervertebral discs of the spine, and the ear. Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue.Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium.In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, [1] and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the
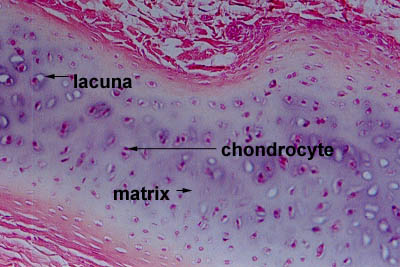
Cartilage, connective tissue forming the mammalian embryonic skeleton prior to bone formation and persisting in parts of the human skeleton into adulthood. It is composed of a dense network of collagen fibers embedded in a gelatinous ground substance. Learn more about the structure and function of cartilage.
Cartilage: What It Is, Function & Types Biology Diagrams
There are three types of cartilage in your body: Hyaline cartilage. Elastic cartilage. Fibrocartilage. Hyaline cartilage. Hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage in your body. It lines your joints and caps the ends of your bones. Hyaline cartilage at the ends of your bones is sometimes referred to as articular cartilage.
