The Importance of Proper Breathing Mechanics through Diaphragmatic Biology Diagrams Quiet breathing occurs at rest and without active thought. During quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles work at different extents, depending on the situation. For inspiration, the diaphragm contracts, causing the diaphragm to flatten and drop towards the abdominal cavity, helping to expand the thoracic cavity.

The diaphragm is the primary muscle involved in breathing, however several other muscles play a role in certain circumstances. These muscles are referred to as accessory muscles of inhalation. External intercostal muscles: Muscles located between the ribs that help the thoracic cavity and pleural cavity expand during quiet and forced inspiration.

The Mechanics of Human Breathing Biology Diagrams
This article examines the mechanics of the muscles that drive expansion or contraction of the chest wall during breathing. The diaphragm is the main inspiratory muscle. When its muscle fibers are activated in isolation, they shorten, the dome of the diaphragm descends, pleural pressure (P(pl)) falls, and abdominal pressure (P(ab)) rises. The relationship between gas pressure and volume helps to explain the mechanics of breathing. There is always a slightly negative pressure within the thoracic cavity, which aids in keeping the airways of the lungs open. During inhalation, volume increases as a result of contraction of the diaphragm, and pressure decreases (according to Boyle

Understanding the diaphragm's role in respiration not only highlights its importance but also sheds light on how breathing mechanics impact overall health. As the diaphragm contracts, it creates a vacuum that allows air to flow into the lungs, while its relaxation helps expel air. Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as abdominal breathing Diaphragm and Intercostal Muscles. The diaphragm is a remarkable muscle, not only due to its role in breathing but also because of its unique structure and function. This thin, dome-shaped sheet of muscle separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and is innervated by the phrenic nerve, which originates in the neck.
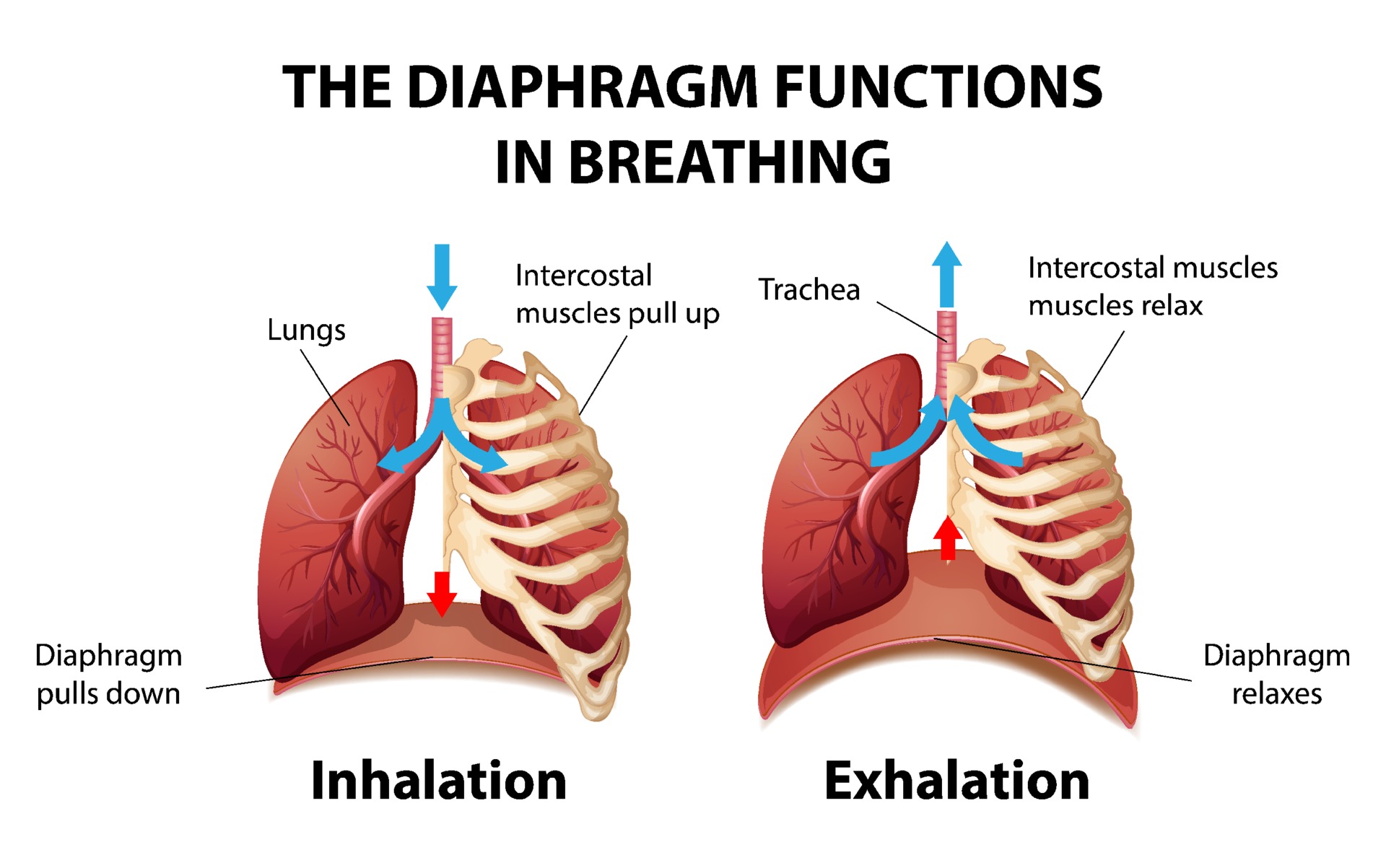
Understanding the Diaphragm's Role in Respiration: Essential Functions ... Biology Diagrams
Mechanics of breathing. When we inhale the intercostal muscles (between the ribs) and diaphragm contract to expand the chest cavity. The diaphragm flattens and moves downwards and the intercostal muscles move the rib cage upwards and out. The mechanics of breathing follow Boyle's Law which states that pressure and volume have an inverse relationship. The process of inhalation occurs due to an increase in the lung volume (diaphragm contraction and chest wall expansion) which results in a decrease in lung pressure in comparison to the atmosphere; thus, air rushes in the airway.
