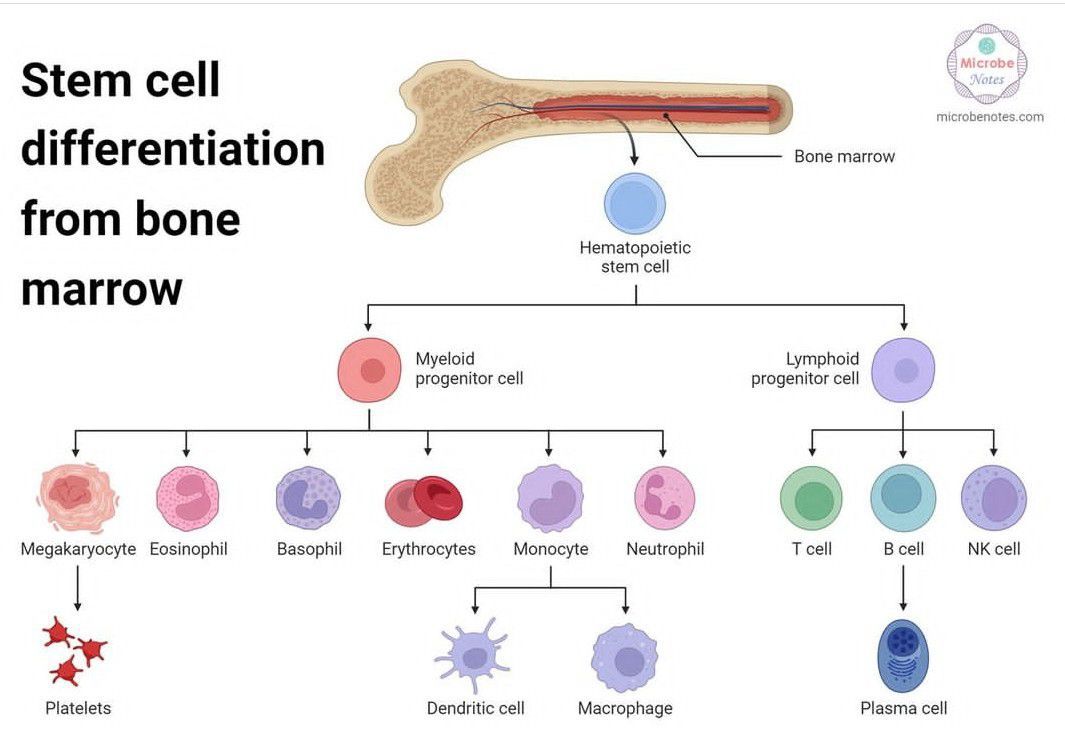
The Different Types of Stem Cells Biology Diagrams The development of multicellular organisms relies on the temporal and spatial control of cell proliferation and cell growth. The relationship between cell-cycle progression and development is complex and characterized by mutual dependencies. On the level of the individual cell, this interrelationshi … Different types of stems cells have varying degrees of potency; that is, the number of different cell types that they can form. Each cycle of subculturing is referred to as a "passage." The original cells can yield millions of stem cells. At any stage in the process, batches of cells can be frozen and shipped to other laboratories for

Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) are uniquely dedicated to rapid, unrestricted proliferation ()(Thomson et al., 1998;Amit et al., 2000;Zwaka and Thomson, 2005).Within the blastocyst of the embryo as well as in culture, hESCs repeatedly traverse the cell cycle and undergo successive symmetrical cell divisions to provide structurally and functionally equivalent progeny cells to retain Hence, this review will address key differences between an abbreviated cell cycle characteristic of embryonic stem cells, as compared with that of somatic cells. In addition, we will highlight differences in molecular organization of the cell cycle of mouse and human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) with the special focus on G1, S, and G2/M-phase Guided Differentiation and Cell Cycle Manipulation of ES cells. To probe the effect of the cell cycle on differentiation we used an ES cell line that constitutively overexpressed the transcription factor MyoD driven off an EF1α promoter activated by tamoxifen-induced Cre recombination. The use of this cell line facilitated our analysis by

Molecular ties between the cell cycle and differentiation in embryonic ... Biology Diagrams
The cell cycle organization of these ground state cells may be different from that of cells cultured in serum/LIF, including a longer G1 phase and the presence of hypo-phosphorylated RB1 37. This surprising finding calls for more side-by-side comparisons between mESCs cultured in different conditions versus pluripotent cells of early embryos in

A stem cell line is a group of cells that all descend from a single original stem cell and are grown in a lab. Cells in a stem cell line keep growing but don't become specialized cells. Ideally, they remain free of genetic defects and continue to create more stem cells. Cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases and other components of the core cell cycle machinery drive cell division. Growing evidence indicates that this machinery operates in a distinct fashion in some mammalian stem cell types, such as pluripotent embryonic stem cells. In this Review, we discuss our curre …
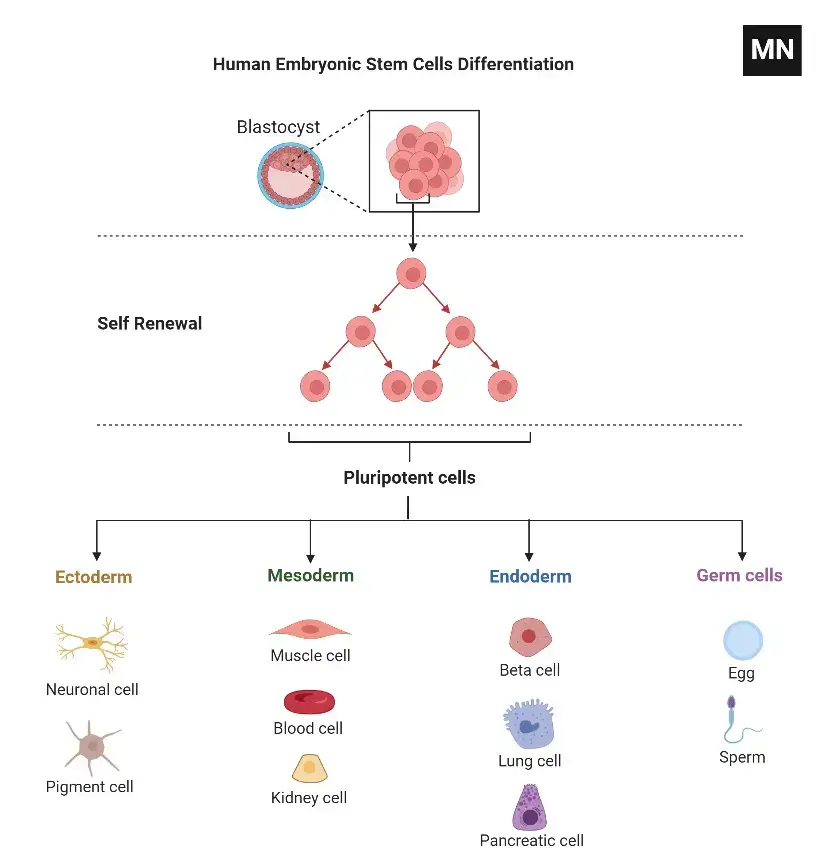
Stem cells: What they are and what they do Biology Diagrams
Embryonic stem cells show unusual cell-cycle features: the duration of the S phase is comparable to somatic cells but they have remarkably short G1 and G2 phases (1-3).In somatic cells, the duration of G1 and G2 is determined by relative levels of Cdk kinase activity and other cell cycle-related proteins ().Many of these proteins, including Cyclin A, Cyclin B, Cdt1, Cdc6, and Geminin The pluripotent cell cycle has characteristics of both embryonic and somatic divisions, and the differences in cell cycle regulation between embryonic stem cells and their differentiated counterparts (summarised in Table 2) likely result from their specific functions. ES cells self-renew and retain the potential to produce all cell types in an