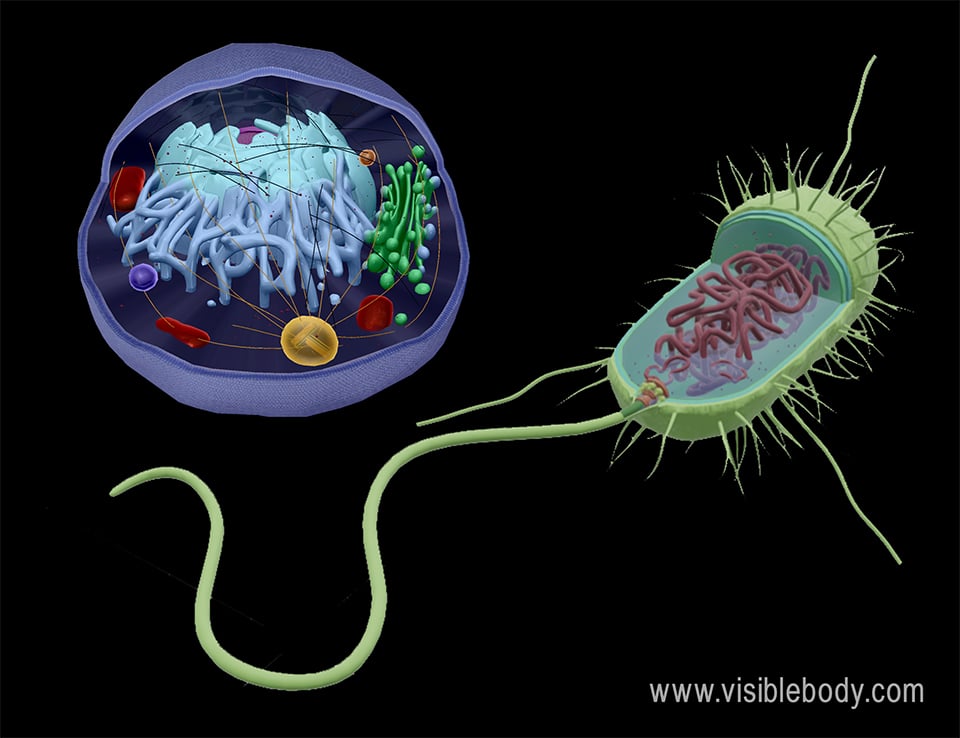
The Cell Cycle and Cell Division Biology Diagrams Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. What is their main difference, and how are they similar. prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in most aspects, such as cell size, shape, organization, and life cycle, including reproduction. The main differences are given below. Monera is a kingdom that includes bacteria and During the 1950s, scientists postulated the concept of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells, with earlier groundwork being laid by Edouard Chatton, a French Biologist in 1925. Anatomically, cells vary with respect to their classification, therefore, prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells differ from each other quite drastically. Read on to The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division is that the prokaryotic cell division occurs through binary fission whereas the eukaryotic cell division occurs either through mitosis or meiosis. Furthermore, prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division are two types of cell division processes classified

This size disparity is due to the complexity and additional organelles present in eukaryotic cells. Furthermore, bacteria have a cell wall composed of peptidoglycan, a unique molecule absent in eukaryotes. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, may have a cell wall made of cellulose (in plants) or chitin (in fungi), but this is not a universal In bacteria, cell growth and DNA replication take place throughout most of the cell cycle, and duplicated chromosomes are distributed to daughter cells in association with the plasma membrane. In eukaryotes, however, the cell cycle is more complex and consists of four discrete phases. Although cell growth is usually a continuous process, DNA is

Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes: Definition and Characteristics Biology Diagrams
Prokaryotes vs eukaryotes: These are two distinct types of cellular organisms. Here is a list of examples for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes: Prokaryotes: Bacteria: Examples include Escherichia coli (E. coli), Bacillus subtilis, The chromatin undergoes dynamic changes during different stages of the cell cycle, allowing for gene The diversity of life on Earth is largely defined by the cellular structures of organisms, with bacteria and eukaryotes representing two fundamental categories. Bacteria, being prokaryotic, exhibit a simpler structural organization compared to the more complex eukaryotic cells found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists.

Differences in Organization. Prokaryotic cells engage in reproduction through a process of cell division called _binary fission_. Eukaryotic cells use a different process of cell division called mitosis, which involves a constant cycle of cell growth and development.. There are frequent checkpoints for the cell to go through, monitoring the cell's external and internal conditions, and Unlike eukaryotes, many bacteria do not have a distinct cell cycle. Consequently, checkpoints that prevent an inopportune shift to the next cell cycle phase do not seem to be generally present Cell growth, replication and fission are illustrated below. 339 Binary Fission. The roughly 30-60 minute life cycle of an actively growing bacterium is not divided into discrete phases. On the other hand, typical eukaryotic cells have a roughly 16-24 hour cell cycle (depending on cell type) that is divided into four separate phases.