Sea Urchin Food Chain Biology Diagrams Shrimp play an essential role in the animal food chain, and without their presence, food webs would be thrown out of balance. Adult shrimps are scavengers. They feed on dead crabs, clams, snails and fish, and worms. In this role, they help rid the ecosystem of dead decaying matter.
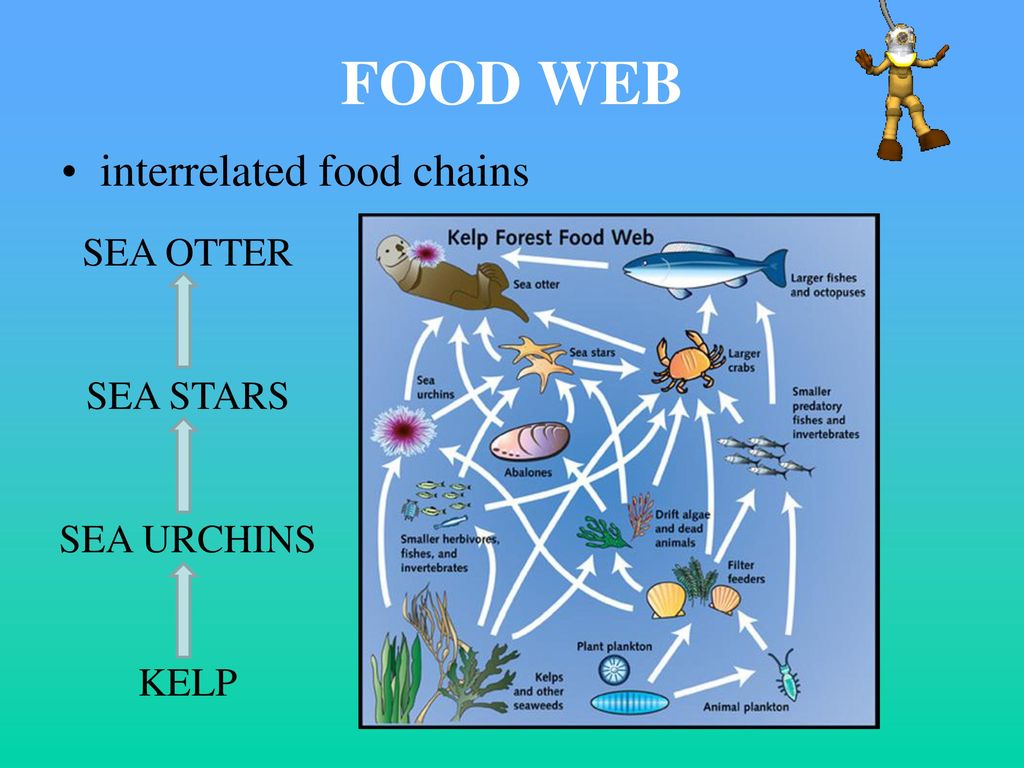
What is a food chain? A food chain shows how energy and nutrients flow through an ecosystem. Every living thing in the world needs food. This shows who eats who in the wild and where that energy comes from. Most food chains begin with the sun. Marine food chain example: Seaweed Copepod (Zooplankton) White Shrimp Croake r Bottlenose Dolphin Blue Shrimp are an essential part of the food chain in aquatic ecosystems. They play a crucial role in the transfer of energy from lower trophic levels to higher trophic levels. Shrimp are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including algae, zooplankton, small fish, and other invertebrates. Food chains can be quite different depending on the type of organism and environment. For example, the ocean food chain, or marine food chain, is a food chain that is based on organisms living in

PDF Food Chains & Food Webs Biology Diagrams
One important fact about shrimp is their role in the marine food chain. Many shrimp species are scavengers, meaning they consume carcasses and decaying matter. While most shrimps are marine creatures that make their home in the vast expanses of the sea, a significant 25% of the global shrimp population surprisingly thrives in inland It's a Fish-Eat-Fish World Some 300,000 marine species are known to science—about 15 percent of all the species identified on the planet. But the sea is so vast that a million or more as yet unknown species may live in its waters. Most of these aquatic species are tied together through the food web. Level One: Photo autotrophs The foundation of the sea's food chain is largely invisible. While most people think of shrimp as sea creatures, some species also live in freshwater lakes, streams, and rivers. While shrimps range in size from microscopic to 18 inches long, they still remain at the bottom of the food chain. Regardless of size, shrimp will always be prey for larger fish and marine life.

Each living thing is a part of multiple food chains - for example, grass is a part of the food chain: grass → grasshopper → frog → snake → eagle. Algae → Shrimp → Tuna → Sea Lion → Killer Whale; Grass → Antelope → Cheetah; Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Small Fish → Dolphin → Shark;
