Role of Mechanotransduction in Vascular Biology Biology Diagrams RhoA signalling in fibrosis. A positive feed-forward cycle is illustrated. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ) is released in response to tissue wounding. Severing the LINC complex, or complete removal of the nucleus, alter a cell's mechanotransduction. Much of the change may be due to reduced RhoA activity. The reason why RhoA activity

Cellular mechanotransduction, a critical regulator of numerous biological processes, is the conversion from mechanical signals to biochemical signals regarding cell activities and metabolism. The mechanically activated cation channels PIEZO1 and PIEZO2 are crucial for mechanotransduction processes in mammals. This Review discusses the structural design and gating dynamics of PIEZO Living cells and tissues experience physical forces and chemical stimuli in a human body. The process of converting mechanical forces into biochemical activities and gene expression is mechanochemical transduction or mechanotransduction. Significant

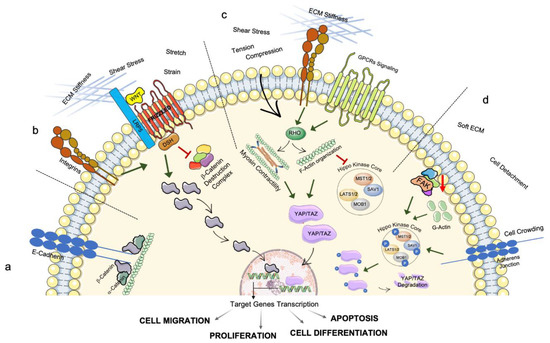
Mechanical Regulation of Transcription: Recent Advances Biology Diagrams
A great deal of this challenge arises from two crucial features of mechanotransduction: that cell and tissue structure both modulate and are sculpted by mechanical stresses, and that there are numerous feedback loops between cell signaling and force generation. (Kip1), and cell cycle progression in human capillary endothelial cells by cell Mechanotransduction and cell-cycle progression. Although the focus on cell-cycle regulation has historically been on biochemical cues, it is becoming increasingly appreciated that mechanical cues play a key role. Cell-cycle progression begins at division completion. Cells will typically either enter the G0 or quiescent phase, in which they do Mechanotransduction is the ability of a cell to sense mechanical cues from its microenvironment and convert them into biochemical signals to elicit adaptive transcriptional and other cellular responses. Here, we describe recent advances in the field of mechanical regulation of transcription, highlight mechanical regulation of the epigenome as a key novel aspect of mechanotransduction, and

Mechanosensing occurs through a series of steps that involve adhesion formation, probing, and response. The cycle begins when (A1-A2) the cell contacts RGD ligand and forms integrin clusters that activate actin polymerization (4, 44).(B1-B4) Step-by-step mechanosensing of fibroblast cells on supported lipid bilayers (45, 114).(C1-C3) When the cell edge encounters new matrix, it forms In nonhematopoietic mammalian cell types, cell cycle progression requires adhesion and spreading on a solid substratum. Loss of this requirement for anchorage correlates closely with tumorigenicity in vivo and is related to the ability of cancer cells to invade and metastasize into other tissues (Huang and Ingber, 1999). Since the main annotation for YAP/TAZ transcription targets lies within the proliferation category, the activity of Hippo effectors in the nucleus has been historically associated with cell growth and tumor spreading (Zanconato et al., 2015), while our group and others lately proved that the mechanotransduction role of YAP is to be ascribed to