Right atrium The Anatomy of the Heart Visual Atlas page Biology Diagrams Basic anatomy of the heart. The heart is at the center of this system, as it pumps blood through vascular channels towards the target tissue. Recall that the heart is a roughly pyramidal organ made up of two muscular pumps that are connected in-series - namely, the left and right heart.Each pump contains an upper chamber that functions as a receptacle for incoming blood, called the atrium
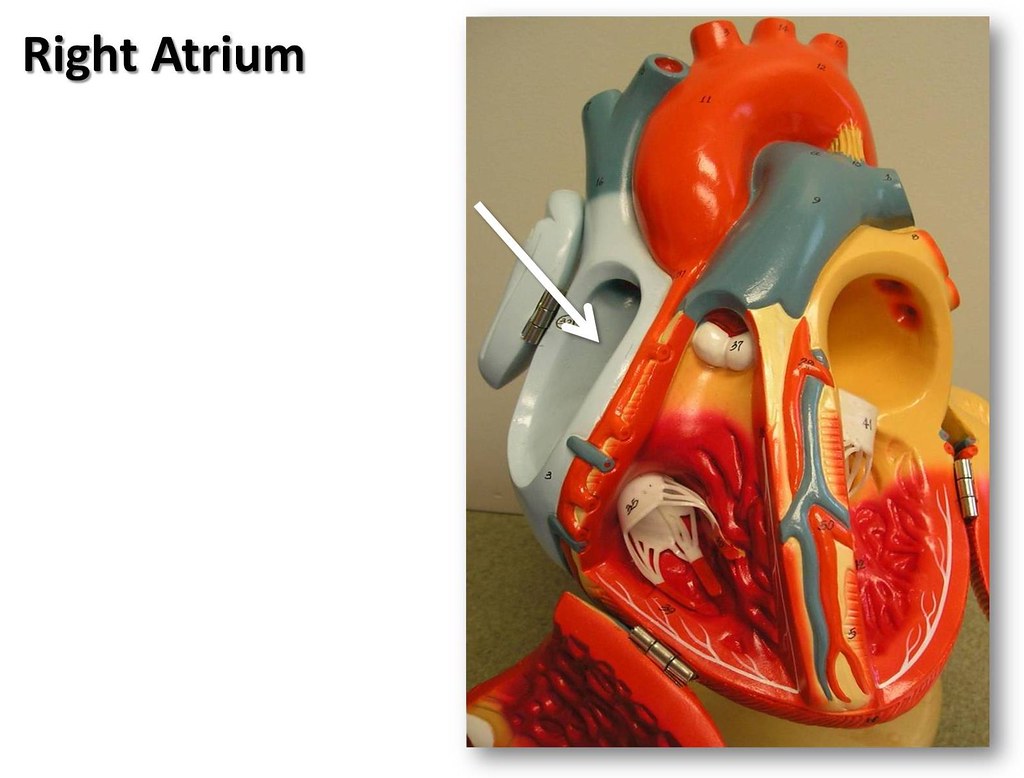
The human heart consists of four chambers: The left side and the right side each have one atrium and one ventricle. Each of the upper chambers, the right atrium (plural = atria) and the left atrium, acts as a receiving chamber and contracts to push blood into the lower chambers, the right ventricle and the left ventricle. Clinical Relevance Atrial Septal Defect. An atrial septal defect is an abnormal opening in the interatrial septum, persistent after birth. The most common site is the foramen ovale, and this is known as a patent foramen ovale.. In the adult, left atrial pressure is usually greater than that of the right atrium, so blood is shunted through the opening from left to right. Figure 3. A. Viewed from the front, the right atrium and right ventricle overlaps the left atrium and left ventricle. The atrial chambers are to the right of their respective ventricular chambers. B. The four cardiac valves are at different levels and different planes with the pulmonary(P) valve situated the most cephalad.
Chambers of the Heart Biology Diagrams
Right ventricle. Blood from your right atrium passes through your tricuspid valve and into your right ventricle. Your right ventricle quickly goes into action by forcefully pumping this blood through your pulmonary valve into your pulmonary arteries and out to your lungs.In your lungs, your blood receives the oxygen it needs to nourish the rest of your body. The heart has five surfaces: base (posterior), diaphragmatic (inferior), sternocostal (anterior), and left and right pulmonary surfaces. It also has several margins: right, left, superior, and inferior: The right margin is the small section of the right atrium that extends between the superior and inferior vena cava. The superior chambers consist of the right atrium and left atrium (plural, atria: L., corridor). which lie primarily on the posterior side of the heart.[Interior view/ Posterior view]Have you been making any of the common anatomy learning mistakes? Find out!

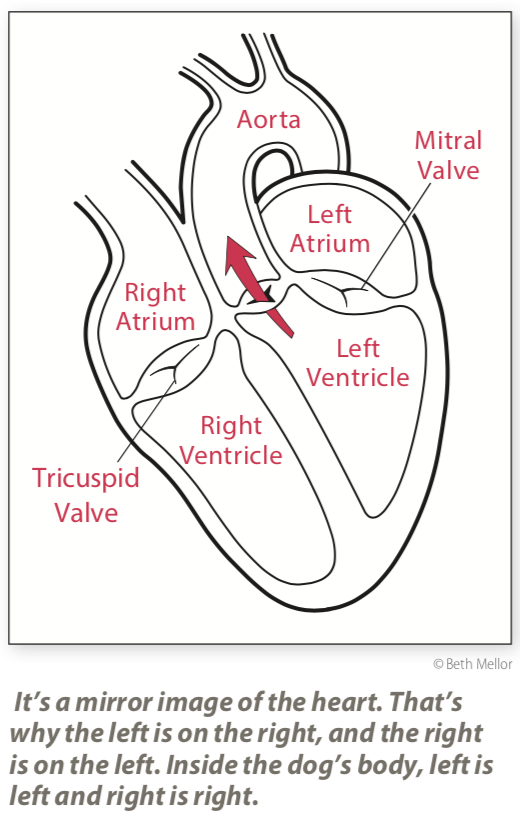
Internally, the heart is divided into four chambers: . Two upper chambers known as atria: right atrium (RA) and left atrium (LA);; Two lower chambers called ventricles: right vetricle (RV) and left ventricle (LV).; Functionally, the heart consists of two pumps (right and left), each consisting of an atrium and a ventricle separated by an atrioventricular valve. The heart is divided into four chambers: left and right atria and ventricles. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body and pumps this blood into the right ventricle. The lungs send the oxygenated blood to the left atrium, which pumps this blood into the left ventricle.
