NLC Science G8 Lesson 19 Food Chains in Yellowstone Biology Diagrams Food Web of Yellowstone National Park. Yellowstone National Park, renowned for its unique ecosystems and diverse species, presents one of the most intricate food webs in North America.Situated at the heart of the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem (GYE), it harbors an array of plant and animal life, from microscopic organisms to top predators.The interactions between these organisms create a

Yellowstone is home to an estimated 10,000-20,000 Elk in the summer and are the most popular ungulate in the park. Elk comprise 90% of all wolf kills and are extremely important in providing food for grizzly bears, mountain lions and at least a dozen other scavenger animals.
Yellowstone National Park Biology Diagrams
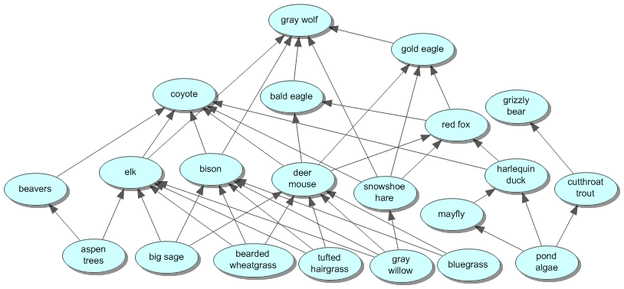
Yellowstone National Park is home to a multitude of primary consumers. Primary consumers are organisms that get their energy from producers (autotrophs). They are considered the first heterotroph on the food chain. Included in the food web above, the primary consumers include pronghorns, beavers, elk, cutthroat trout, mayflies, and deer mice. Yellowstone National Park is a region with abundant and diverse wildlife. Wolves and bears are at the top of the Yellowstone food chain, and prey on other animals such as elk and bison. Other

Yellowstone National Park Food Chain (Forest) In Conclusion The food chain needs all of the producers and consumers to keep all of the chain working and if something in the chain is gone the rest will slowly die out. The Food Chain Breaking Yellowstone workers did an experiment.
![[FREE] The diagram shows part of the food web in Yellowstone National ... Biology Diagrams](https://media.brainly.com/image/rs:fill/w:750/q:75/plain/https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d38/6673be60241e28a7326535177973c03d.png)
Food Webs, Energy Flow, Carbon Cycles, and Trophic Pyramids Biology Diagrams
To begin this hands-on, minds-on activity, students view a video about changes in the ecosystem that resulted when wolves were eliminated from Yellowstone National Park and decades later returned to Yellowstone. Students learn about food chains and food webs, and they construct and analyze a food web for Yellowstone. In Yellowstone National Park, a notable example of a trophic cascade involves the interactions between three organisms: black oak trees, mule deer, and wolves. Here's how these organisms fit into a simple food chain structure: Producers: Black Oak Trees . These trees are primary producers that convert sunlight into energy through Greater Yellowstone's diversity of natural wealth includes hydrothermal features, wildlife, vegetation, lakes, and geologic wonders like the Grand Canyon of the Yellowstone River. Heart of an Ecosystem. Yellowstone National Park was established in 1872 primarily to protect geothermal areas that contain about half the world's active geysers.
