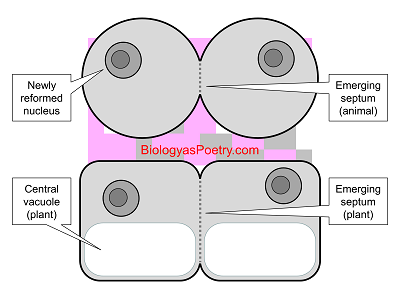
How is plant cell cytokinesis different from animal cell cytokinesis Biology Diagrams Cytokinesis, in biology, the process by which one cell physically divides into two cells. Cytokinesis represents the major reproductive procedure of unicellular organisms, and it occurs in the process of embryonic development and tissue growth and repair of higher plants and animals. Cytokinesis Definition. Cytokinesis is the final process in eukaryotic cell division, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles, and cellular membrane. Cytokinesis typically occurs at the end of mitosis, after telophase, but the two are independent processes. Cytokinesis illustration Cilliate undergoing cytokinesis, with the cleavage furrow being clearly visible.. Cytokinesis is the division of cells after either mitosis or meiosis I and II.. During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm (the liquid center of the cell that holds the organelles into place) splits into two equal halves, and the cell becomes two daughter cells. . This occurs right after the
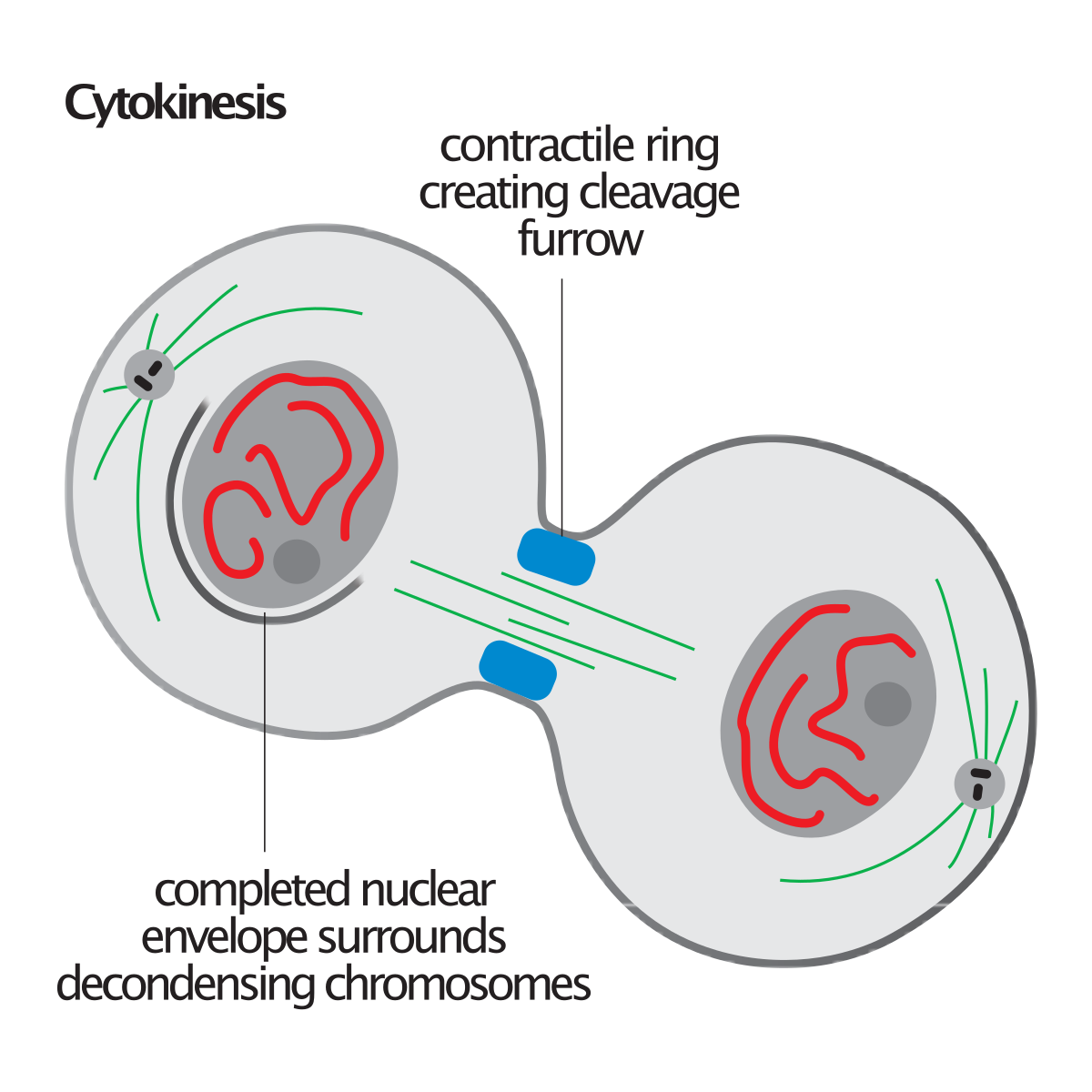
Cytokinesis is the final stage in the cell cycle, when a new generation of daughter cells is formed through the splitting of the cytoplasm and the separation of the two identical cells. This signals the start of a new cellular generation. For any organism to grow and survive, it requires new cells to be formed. A human embryo—a single cell Cytokinesis is the physical division of the cell cytoplasm, the cell membrane, and cell organelles in eukaryotic cells to produce two distinct cells at the end of the cell cycle in both mitosis and meiosis. In most cells, cytokinesis is initiated during the anaphase stage and ends in telophase, a phase where the chromosomes are completely
Description & Process Biology Diagrams
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle is comprised of these fundamental events: (1) resting phase (Gap 0), (2) interphase (Gap 1, S phase, Gap 2), and (3) cell division (i.e. mitotic phase and cytokinesis).In essence, the cell may enter a quiescent stage called the resting phase or it may go through the rest Cytokinesis is the final step of the cell division process of a eukaryotic cell when the parent cell cytoplasm divides to form two daughter cells. It occurs in tandem with two types of nuclear divisions: mitosis and meiosis.The primary purpose of cytokinesis is to ensure that one nucleus ends up in each daughter cell after division. Cytokinesis illustration Ciliate undergoing cytokinesis, with the cleavage furrow being clearly visible.. Cytokinesis (/ ˌ s aɪ t oʊ k ɪ ˈ n iː s ɪ s /) is the part of the cell division process and part of mitosis during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division in

Definition of Cytokinesis: Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm of the parent cell into two daughter cells at the end of mitosis or meiosis. Explanation. Initiation . The contractile ring initiates and starts to build a cleavage furrow. This happens in the anaphase. The cell cycle culminates in the division of the cytoplasm by cytokinesis. In a typical cell, cytokinesis accompanies every mitosis, although some cells, such as Drosophila embryos (discussed later) and vertebrate osteoclasts (discussed in Chapter 22), undergo mitosis without cytokinesis and become multinucleate. Cytokinesis begins in anaphase and ends in telophase, reaching completion as the