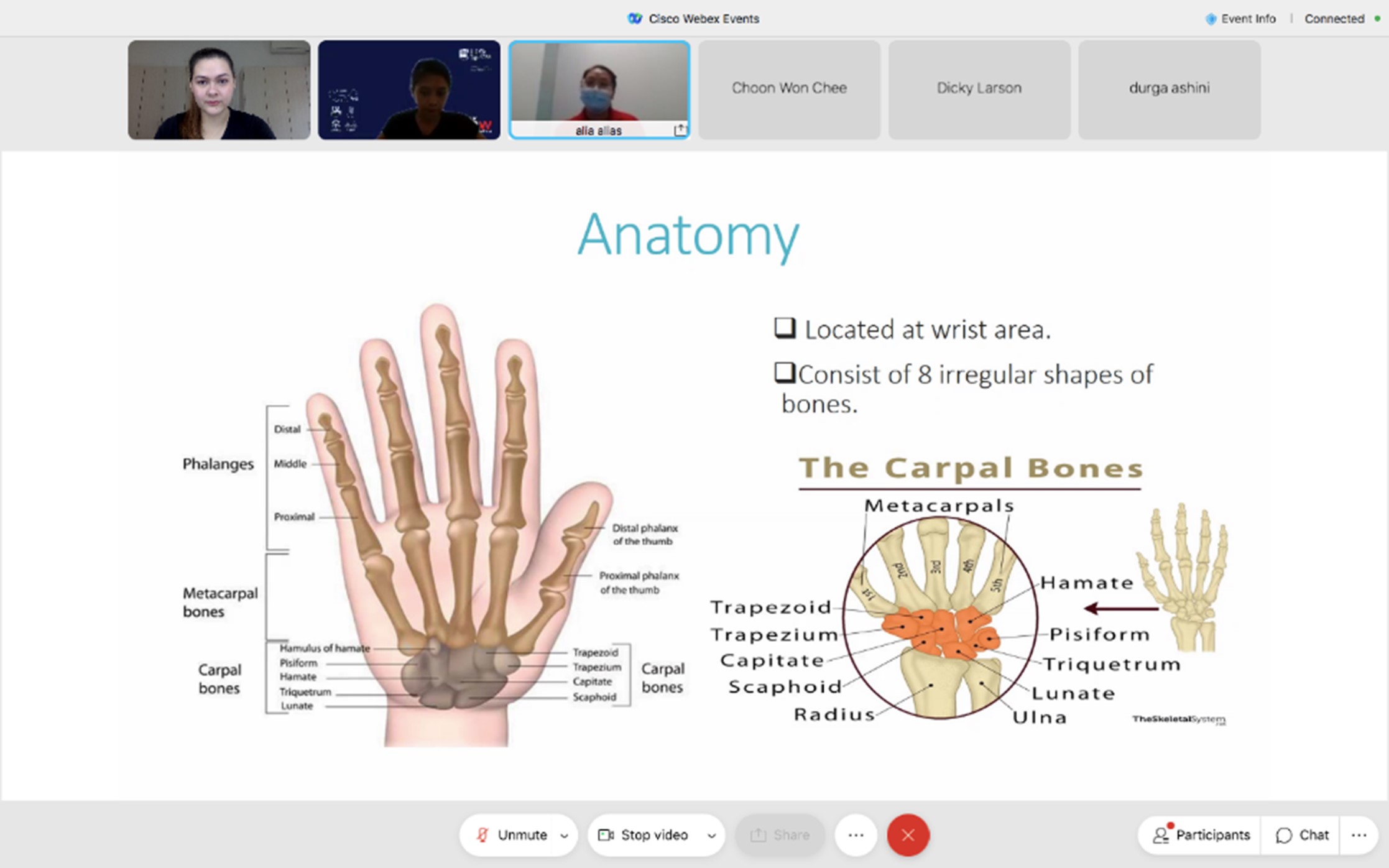
Hand Wrist Elbow Shoulder Biology Diagrams Introduction. The wrist joint connects the distal end of the radius to the carpal bones in the hand. It is a synovial joint, meaning the bones are separated by a narrow cavity filled with synovial fluid.. The wrist joint is an articulation of the distal head of the radius, the articular disc that overlies the distal ulna, and the proximal carpal bones of the hand (scaphoid, lunate and triquetrum). The carpal tunnel is an osseofibrous channel (a) located in the volar portion of the wrist. The floor of the tunnel is formed by the carpal bones; the roof by the flexor retinaculum (B, D: Axial T1-weighted MRI scan; C, E: ultrasound). The tendons of the flexor pollicis longus (Flp), the superficial (Fs) and deep (Fp) flexors of the fingers
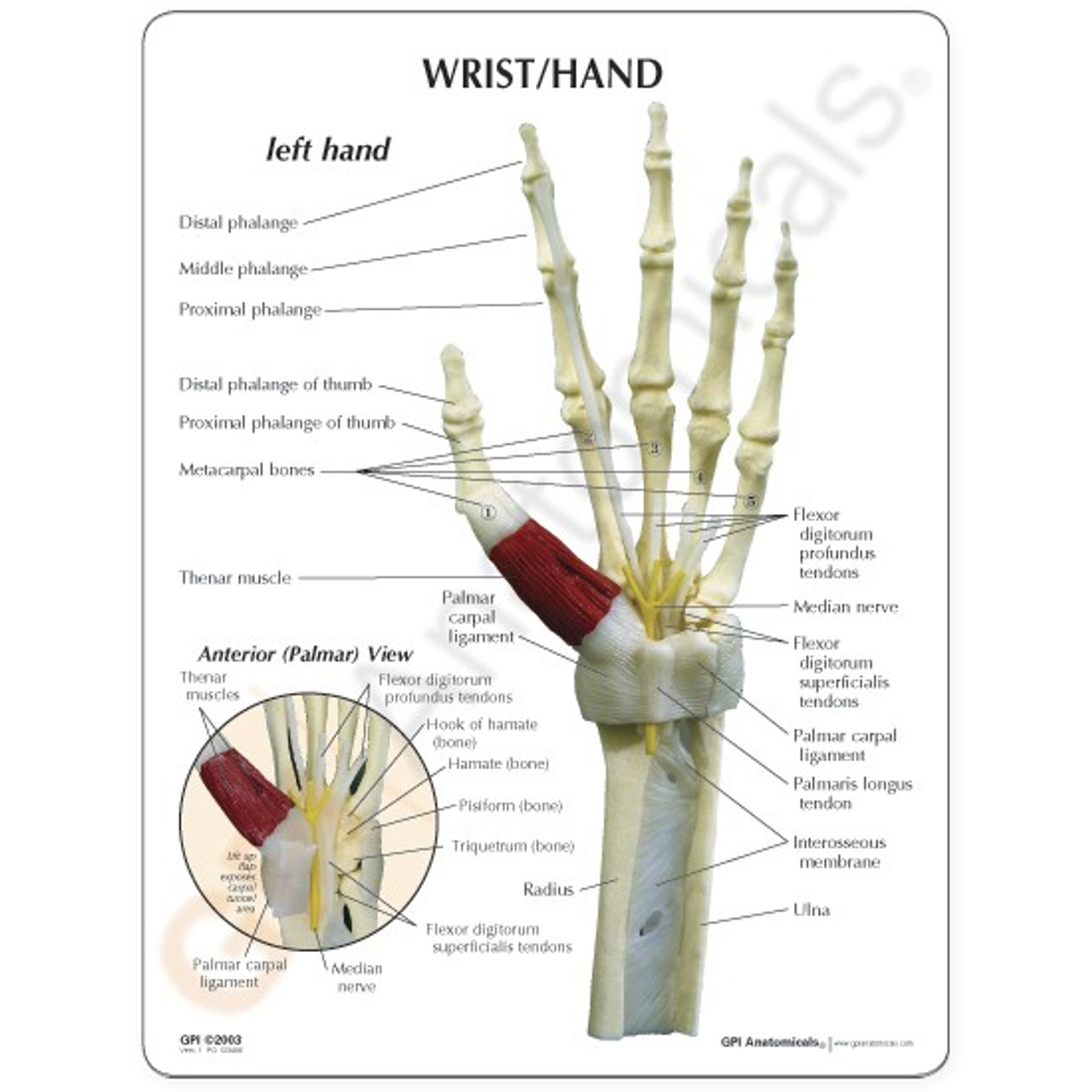
Carpal tunnel. Carpal tunnel. Formed by four carpal bones and the flexor retinaculum, the carpal tunnel forms as a deep arch on the anterior surface of the wrist.. Medially, it is formed by the pisiform and hook of the hamate bones, while laterally, it is formed by the tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium bones.; Both sides of the carpal arch are connected by the flexor retinaculum, a thick The carpal tunnel is a narrow osteofibrous canal located on the palmar side of the wrist, found deep to the flexor retinaculum. The floor of the carpal tunnel is composed of the carpal bones, which is how it got its name.. The carpal tunnel serves as a passageway for structures passing between the anterior forearm and the hand.It transmits the median nerve and the tendons of the flexor Carpal bones are a group of eight small, irregularly shaped bones that form the wrist (carpus). These bones are arranged in two rows: a proximal row (closer to the forearm) and a distal row (closer to the hand).The carpal bones collectively provide flexibility and stability to the wrist, enabling a wide range of movements. [2] The eight carpal bones are the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum

Carpal tunnel and structures at the wrist Biology Diagrams
The Carpal Tunnel. The carpal tunnel is a passageway for the medial nerve, as well as nine tendons passing from the wrist into the hand and fingers [11]. It is located on the palmar side of the wrist, with its boundaries formed by the carpal bones and the flexor retinaculum (a fibrous band arching over the carpal bones on the palmar side) [12].
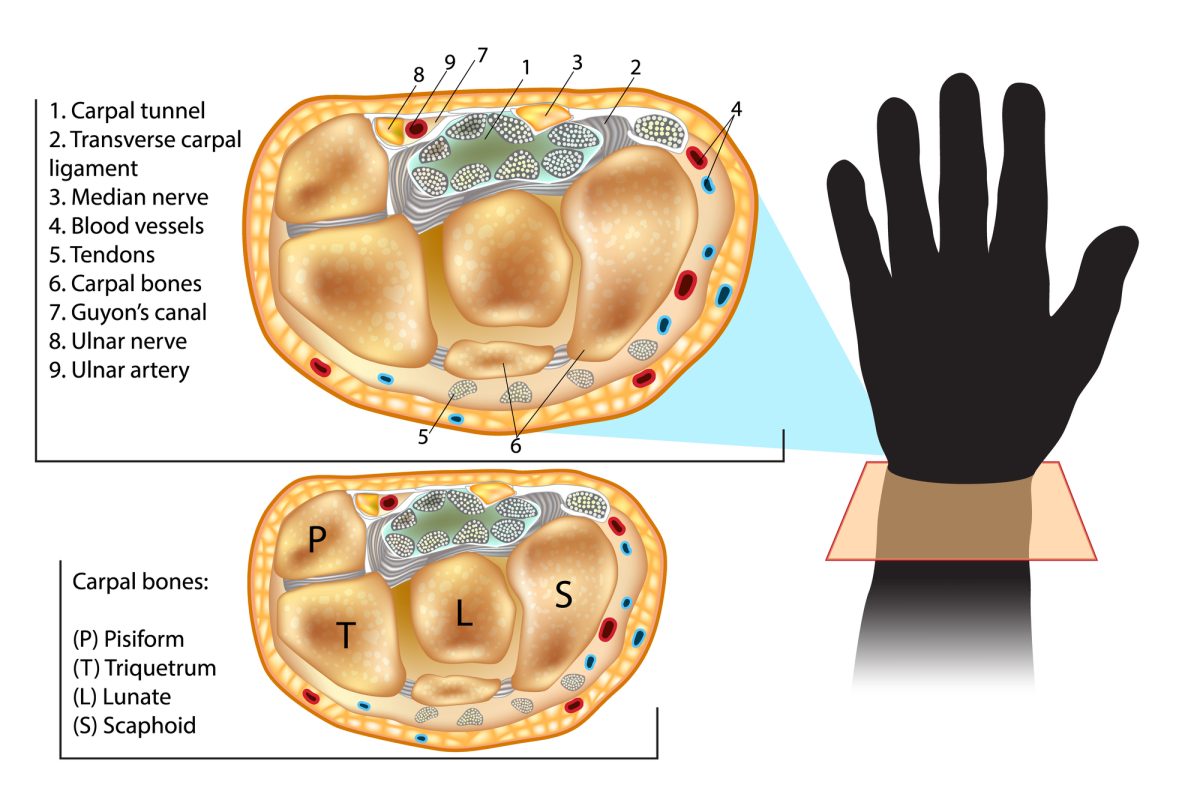
The carpal tunnel is an osteofibrous canal situated in the volar wrist. The boundaries are the carpal bones and the flexor retinaculum (A). The carpal tunnel contains nine tendons: the flexor pollicis longus, the four flexor digitorum superficialis and the four flexor digitorum profundus as well as the median nerve (B, C). Anatomy Limits. The carpal tunnel is a non-extendible osteofibrous tunnel defined as the space located between the flexor retinaculum, which forms the roof, and the carpal sulcus, which forms the base. 61 pressure is applied using two fingers on the median region of the carpal tunnel, with the wrist flexed at 60°, elbow extended and

Carpal Bones (Wrist Bones): Definition, Names, Anatomy, Diagram Biology Diagrams
Turns the carpal arch into the carpal tunnel by bridging the space between the medial and lateral parts of the arch. Spans between the hook of hamate and pisiform (medially) to the scaphoid and trapezium (laterally). To find where the carpal tunnel begins on yourself, locate your distal wrist crease, which aligns with the entrance of the carpal The carpal tunnel (carpal canal) is the passageway on the palmar side of the wrist that connects the forearm to the middle compartment of the deep plane of the palm.The carpus, the bony elements of the wrist, form an arch which is convex on the dorsal side of the hand and concave on the palmar side. The groove on the palmar side, the sulcus carpi, is covered by the flexor retinaculum, a sheath