Evolutionary Dynamics of Mutator Phenotypes in Cancer Implications for Biology Diagrams Cancer is a systemic manifestation of aberrant cell cycle activity and dysregulated cell growth. Genetic mutations can determine tumor onset by either augmenting cell division rates or restraining normal controls such as cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. As a result, tumor cells not only undergo uncontrolled cell division but also become compromised in their ability to exit the cell cycle

This study is a cross-cancer type analysis of the effects of TP53 mutations on gene expression. A hierarchical cluster analysis of the expression profile of the p53 signaling pathway classified 21 Many other mutations have no effect on the organism because they are repaired beforeprotein synthesis occurs. Cells have multiple repair mechanisms to fix mutations in DNA. It is generally caused by mutations in genes that regulate the cell cycle. Because of the mutations, cells with damaged DNA are allowed to divide without limits. A mutation in one proto-oncogene would not cause cancer, as the effects of the mutation would be masked by the normal control of the cell cycle and the actions of tumor suppressor genes. Similarly, a mutation in one tumor suppressor gene would not cause cancer either, due to the presence of many "backup" genes that duplicate its functions.

The cell cycle: a review of regulation, deregulation and therapeutic ... Biology Diagrams
Cell cycle deregulation associated with cancer occurs through mutation of proteins important at different levels of the cell cycle. In cancer, mutations have been observed in genes encoding CDK, cyclins, CDK shows an anti‐proliferative effect on human tumour cell lines and has now entered clinical trials (Takahashi et al. 1989

Different p53 mutations and their potential effects on its function and oncogenic activity. Mutation of TP53 genes is associated with inactivation of wild-type TP53 gene and 75% of P53 mutations lead to loss of p53 functions. Inactivation of the wild type function of p53 promotes invasion, proliferation, cell survival, cancer progression, and metastasis.
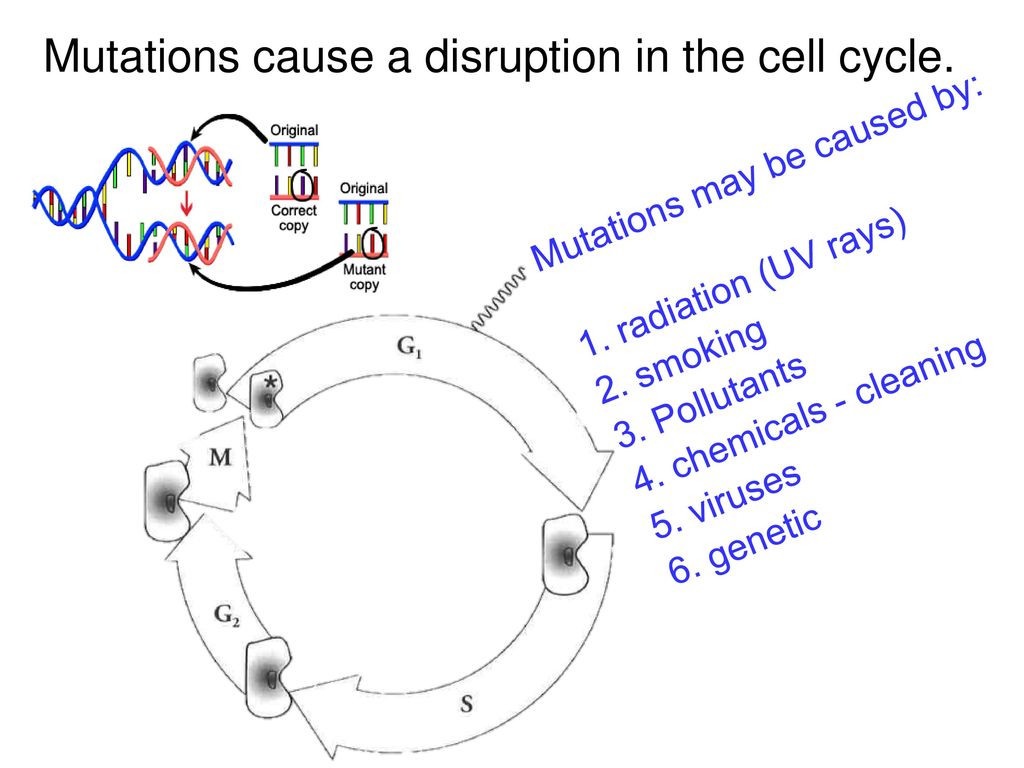
Different impacts of TP53 mutations on cell cycle Biology Diagrams
The inhibitory effects on cell growth are consistent across different cancer types carrying diverse p53 mutations. Furthermore, CP-31398 has been shown to increase ROS production, triggering apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells regardless of p53 status ( 121 ). Cancer-associated mutations that perturb cell cycle control allow continuous cell division chiefly by compromising the ability of cells to exit the cell cycle. recapitulates the effect of
