E3 Ubiquitin Ligases as Immunotherapeutic Target in Biology Diagrams Later in 2003, human enhancer of invasion 10 (HEI10) was first identified as a RING-finger family ubiquitin ligase that regulates cell cycle by interacting with cyclin B1 and promoting its degradation, Reed S.I. Ubiquitin ligases and cell cycle control. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013;82:387-414. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060410-105307.
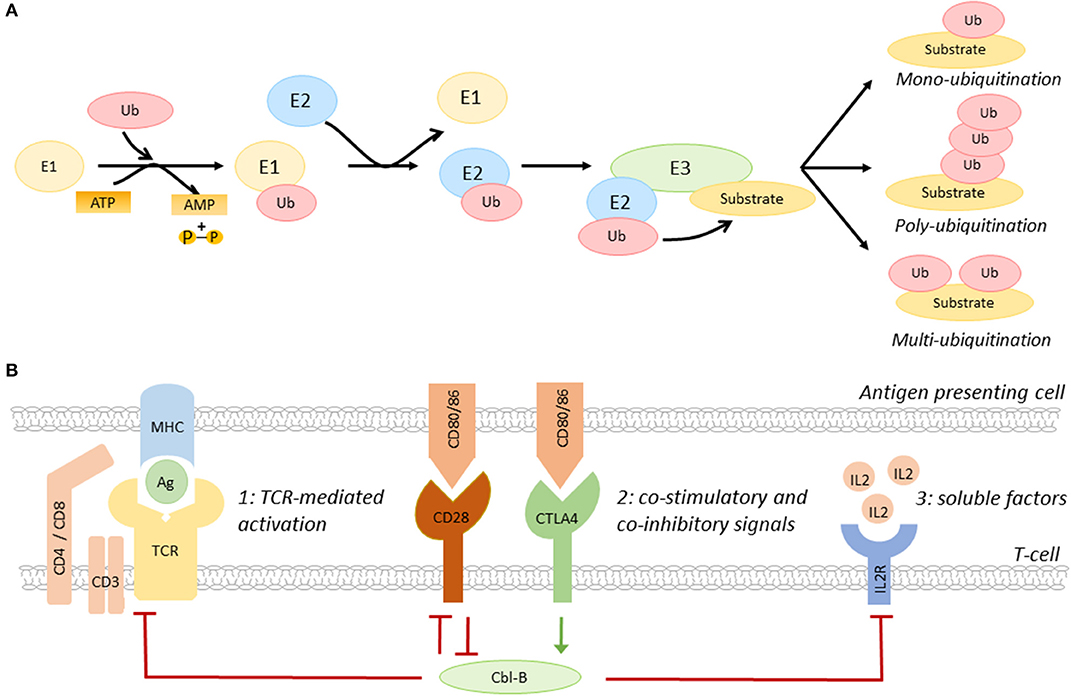
The ubiquitin-proteasome system plays a pivotal role in the sequence of events leading to cell division known as the cell cycle. Not only does ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis constitute a critical component of the core oscillator that drives the cell cycle in all eukaryotes, it is also central to the mechanisms that ensure that the integrity of the genome is maintained. The rapid removal of positive regulators prevents them from interfering with regulation of subsequent cell cycle events. In this review, we highlight the recent advances of our understanding of how a recently discovered ubiquitin ligase, designated SCF, contributes to mammalian cell cycle control. The ubiquitin-proteasome system plays a pivotal role in the sequence of events leading to cell division known as the cell cycle. Not only does ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis constitute a critical component of the core oscillator that drives the cell cycle in all eukaryotes, it is also central to the mechanisms that ensure that the integrity of the genome is maintained. These functions are

The ubiquitin proteasome system — Implications for cell cycle control ... Biology Diagrams
Several ubiquitin ligases are altered in cancer. These proteins are crucial for the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of cell-cycle proteins, ensuring regulated progression through the cycle.
Abstract. Two families of E3 ubiquitin ligases are prominent in cell cycle regulation and mediate the timely and precise ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent degradation of key cell cycle proteins: the SCF (Skp1/Cul1/F-box protein) complex and the APC/C (Anaphase Promoting Complex or Cyclosome).

Implications for cell cycle control ... Biology Diagrams
Here, we will mainly focus on summarizing the physiological role of the ubiquitin signaling in cell cycle control and tumorigenesis, with primary purpose to provide a better understanding of A driving force of the cell cycle is the activation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), the activities of which are controlled by the ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of key regulators such as cyclins and CDK inhibitors. Two ubiquitin ligases, the SKP1-CUL1-F-box-protein (SCF) complex and the anaphase … • Two major classes of ubiquitin ligases, the SKP1-CUL1-F-box-protein (SCF) complex and the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), have a central role in cell-cycle regulation.

The APC/C is a prominent E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in cell cycle regulation. It consists of thirteen different subunits and, in somatic cells, has two co-activators: Cdc20 and Cdh1 CRL4 Cdt2 is further involved in cell cycle control via regulation of histone methylation by ubiquitylation of Set8. Set8 mono-methylates Lys 20 of histone H4
