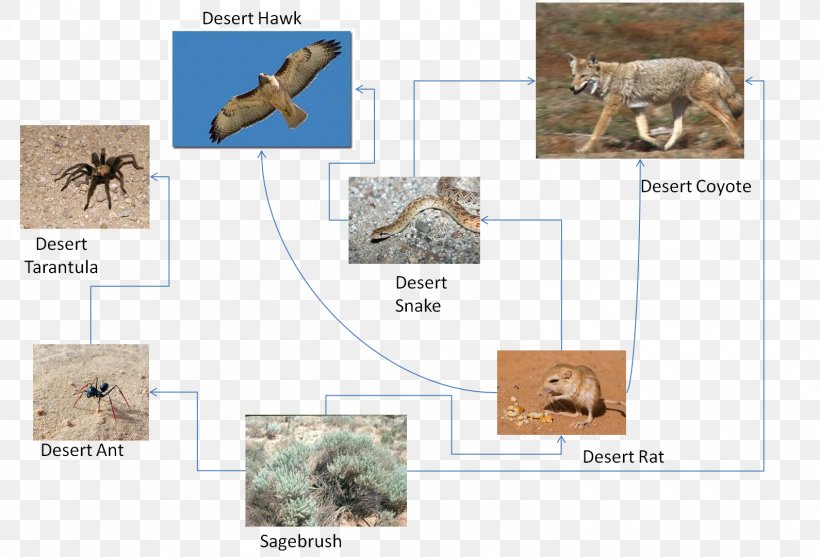
Desert Biome Food Chain by Ethan Silver on Prezi Biology Diagrams A desert food chain is a graphical representation showing who eats whom and thus the flow of energy in the desert biome. Like other food chains, there are two main types of organisms in a desert food chain: producers and consumers. The desert food chain and food web show how organisms adapt to survive and thrive in this extreme environment. The desert food chain shows how plants and animals rely on each other in dry places, like cacti and coyotes. This article will provide an in-depth look at the various trophic levels of the fascinating, intricate desert ecosystem. Learn about the coyote, its habitat, diet, behavior, and adaptability in diverse environments. Discover its role as an opportunistic predator in the wild.

Explore how energy flows through desert food chains, involving producers, consumers, and predators. Learn about desert ecosystems and food webs.

Sonoran Desert Fact Sheet Biology Diagrams
The bug ate the daisy that grew on the desert plain, Where the sun helped it grow and so did the rain - Links in a food chain. There once was a coyote, and I'll make a bet, He'd eat anything he could possibly get. The coyote ate the snake who often grabbed birds, And swallowed them whole, or so I have heard. The snake are the wren who gobbled up bugs, And creepies and crawlies and

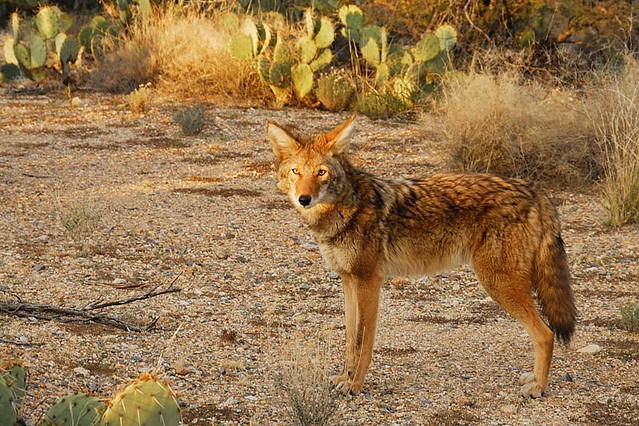
Creatures like the gray fox, kit fox, elf owl, red-tailed hawk, scorpion, roadrunner, rattlesnake, and spiders form this link in the chain. Many food chains have tertiary and even quaternary consumers, and some animals like the coyote will fill multiple roles depending on what's available and on the menu. In the Sonoran Desert, coyotes vary their diet with the seasons. Some of their favorite foods include cactus fruits, mesquite beans, flowers, insects, rodents, lizards, rabbits, birds, and snakes. As a top predator, coyotes play an important role in maintaining balance in an ecosystem's food web. The top of the desert food chain does eventually die though, and is returned to the bottom of the chain as nutrients by decomposes.The energy from the sun is used by the plants, and then the

Desert Food Chains and Ecosystems Biology Diagrams
The food chain shown above depicts the relationship between predators (animals who naturally prey on other species) and their prey, such as herbivores (plant-eating organisms) in the desert. This chain shows a jackrabbit, an herbivore, eating the leaves of a bush. The energy the rabbit received from the bush is then transferred to the fox when the jackrabbit is eaten by it. The coyote hunts ecological This occurs parlance, through "trophic a series of interactions among species in the food chain, or in of food chain, or at the highest cascades." They work as follows. raccoons, opossums, striped skunks, "trophic" and red foxes, level. Coyotes which Coyotes on mesopredators, are at the top