CH 12 NOTES part 2 Regulation of the Cell Cycle PowerPoint Biology Diagrams Understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms both internal and external to the cell; Explain how the three internal control checkpoints occur at the end of G 1, at the G 2 /M transition, and during metaphase; Describe the molecules that control the cell cycle through positive and negative regulation A collection of new reviews and protocols from leading experts in cell cycle regulation, Cell Cycle Control: Mechanisms and Protocols, Second Edition presents a comprehensive guide to recent technical and theoretical advancements in the field. Beginning with the overviews of various cell cycle regulations, this title presents the most current protocols and state-of-the-art techniques used to
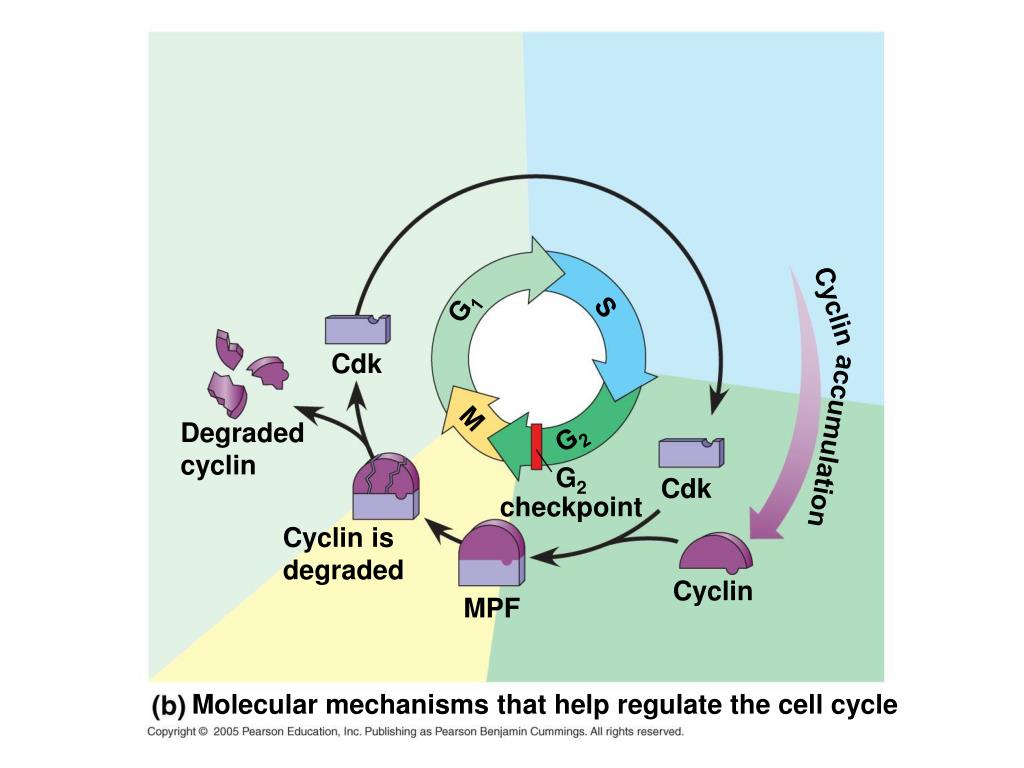
This article reviews the mechanisms that control cell cycle entry and exit, with an emphasis on single cell analysis in mammalian model systems. In the first section, the molecules that enforce cell cycle progression and cell cycle exit are introduced and their mechanistic roles are described. Principles of cell cycle control are explained The cell cycle is controlled by numerous mechanisms ensuring correct cell division. This review will focus on these mechanisms, i.e. regulation of cyclin‐dependent kinases (CDK) by cyclins, CDK inhibitors and phosphorylating events. (2000) Cell cycle control as a basis for cancer drug development. Int. J. Oncol. 16, 871. [Google Scholar To prevent a compromised cell from continuing to divide, there are internal control mechanisms that operate at three main cell cycle checkpoints at which the cell cycle can be stopped until conditions are favorable. Figure 1 The cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. Integrity of the DNA is assessed at the G1 checkpoint.
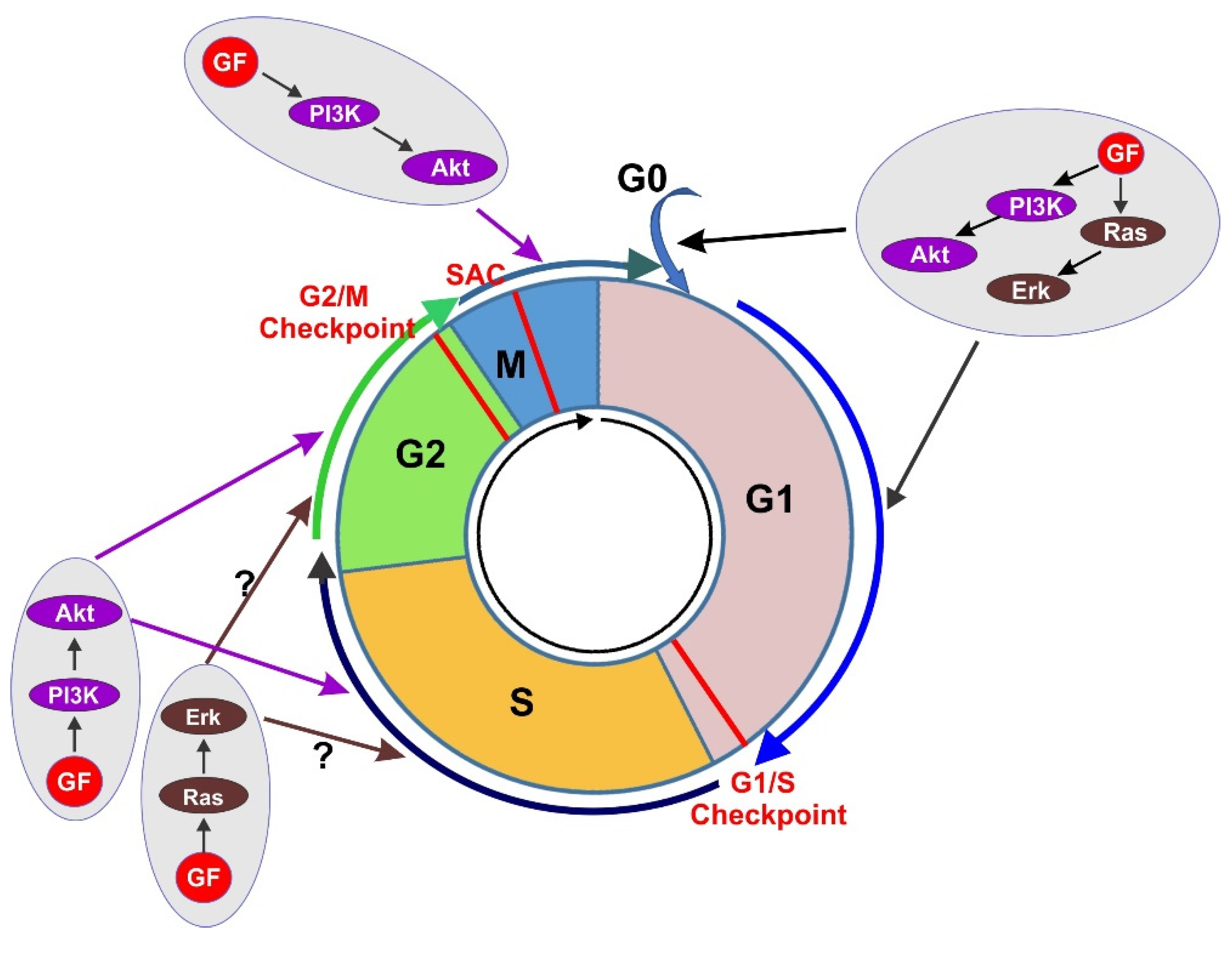
The cell cycle: a review of regulation, deregulation and therapeutic ... Biology Diagrams
In other words, the cell cycle control system is made up of external signals received by a cell and cells internal environment. Signals of cell cycle control: External Signals in Cell Cycle Control. We understand that the cells of the human body communicate with each other. Cell communication is a part of the regulation and coordination system. Understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms both internal and external to the cell; Explain how the three internal control checkpoints occur at the end of G 1, at the G 2 /M transition, and during metaphase; Describe the molecules that control the cell cycle through positive and negative regulation The Cell-Cycle Control System Triggers the Major Processes of the Cell Cycle. The cell-cycle control system operates much like the control system of an automatic clothes-washing machine. The washing machine functions in a series of stages: it takes in water, mixes it with detergent, washes the clothes, rinses them, and spins them dry.These essential processes of the wash cycle are analogous to

The choice depends on cell cycle phase and damage extent, ensuring the most accurate mechanism is employed. If damage is severe, prolonged checkpoint activation can lead to chromatin remodeling that alters gene expression, reinforcing arrest or initiating apoptosis.