Cell signaling general pathway Diagram Biology Diagrams Cell signaling pathways play a major role in cell division. Cells do not normally divide unless they are stimulated by signals from other cells. The ligands that promote cell growth are called growth factors. Most growth factors bind to cell-surface receptors that are linked to tyrosine kinases. These cell-surface receptors are called receptor

Abstract. Cell division requires careful orchestration of three major events: entry into mitosis, chromosomal segregation, and cytokinesis. Signaling within and between the molecules that control these events allows for their coordination via checkpoints, a specific class of signaling pathways that ensure the dependency of cell-cycle events on the successful completion of preceding events.

Phosphatase Integration: Lessons from Mitosis Biology Diagrams
These four proteins control the localization and activity of Aurora in the cytoplasm and at all key mitotic structures that also serve as signaling platforms (2, 187, 206, 264-266)—centrosomes, spindle MTs, centromeres, kinetochores, the central spindle, and the midbody—and are integral to all four pathways of spindle assembly. We This review uses specific examples from the field of mitosis to highlight key features of a signalling response that rely on cooperativity between kinases and phosphatases (see Box 1 for an overview). We discuss each of these properties in turn from a systems perspective to rationalise why kinase-phosphatase integration is important, before providing examples where this has been shown to be
Explore the intricacies of cell division, focusing on mitosis, cytokinesis, and the regulation processes ensuring accurate cell replication. Home; Anatomy and Physiology; The regulation of the cell cycle is a network of checkpoints and signaling pathways that ensure orderly progression through the phases of cell division. This regulatory Together, these observations coupled with earlier ones, confirmed that cell type specific mitogen signaling strength and duration are linked to critical cell cycle consequences as put forward by Marshall (): Weaker and prolonged are associated to differentiation, short and strong to proliferation ().Cell proliferation depends on mitogenic signaling for passage of the G 1 /S restriction window.

Signaling Pathways that Regulate Cell Division Biology Diagrams
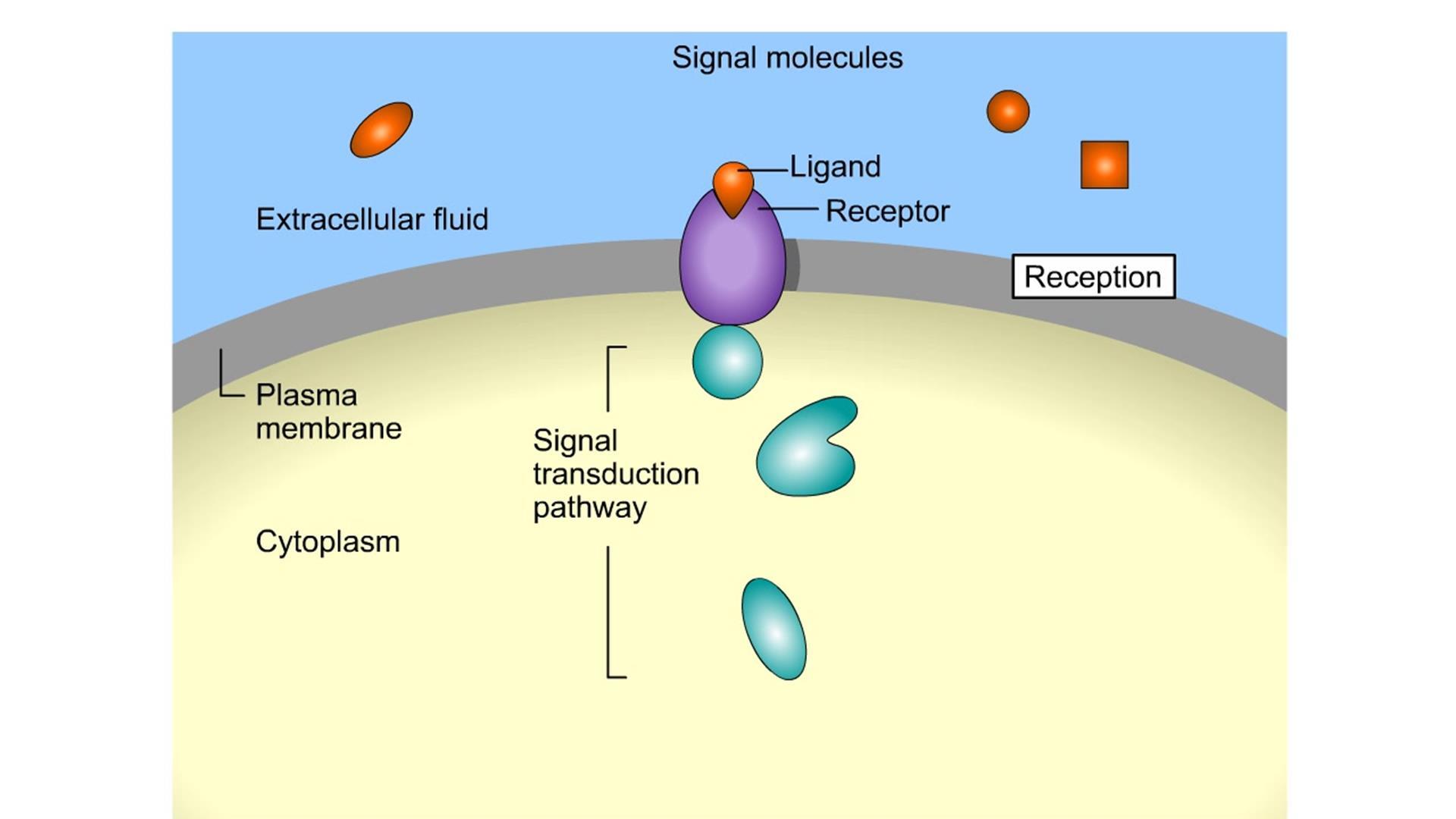
•Cell cycle and Mitosis ATP GTP cAMP Protein kinase A Cellular responses G-protein-linked receptor Adenylyl G protein cyclase 1 Receptor CYTOPLASM Activation of cellular response Relay molecules Signaling molecule 1 2 3 General Signaling Pathway 4. Termination 1. Reception 2. Transduction 3. Response 2 3 Signal molecule Active protein

Abstract. Cells decide to proliferate or remain quiescent using signaling pathways that link information about the cellular environment to the G 1 phase of the cell cycle. Progression through G 1 phase is controlled by pRB proteins, which function to repress the activity of E2F transcription factors in cells exiting mitosis and in quiescent cells. . Phosphorylation of pRB proteins by the G 1 Negative feedback loops are often built into signaling pathways, and CDKs are no different. The mechanism is illustrated in Figure 08-09. APC is phosphorylated by M-CDK so that it is active and controls the metaphase checkpoint. Describe how signaling events are used to end mitosis, starting at anaphase and followed by the transition of the DNA damage activates response pathways through ATM/ ATR and Chk1/2 kinases to block CDK activity, leading to cell cycle arrest and DNA repair or cell death. The G2/M checkpoint prevents cells containing damaged DNA from entering mitosis (M). Activated CDK1 (cdc2) bound to cyclin B promotes entry into M-phase.