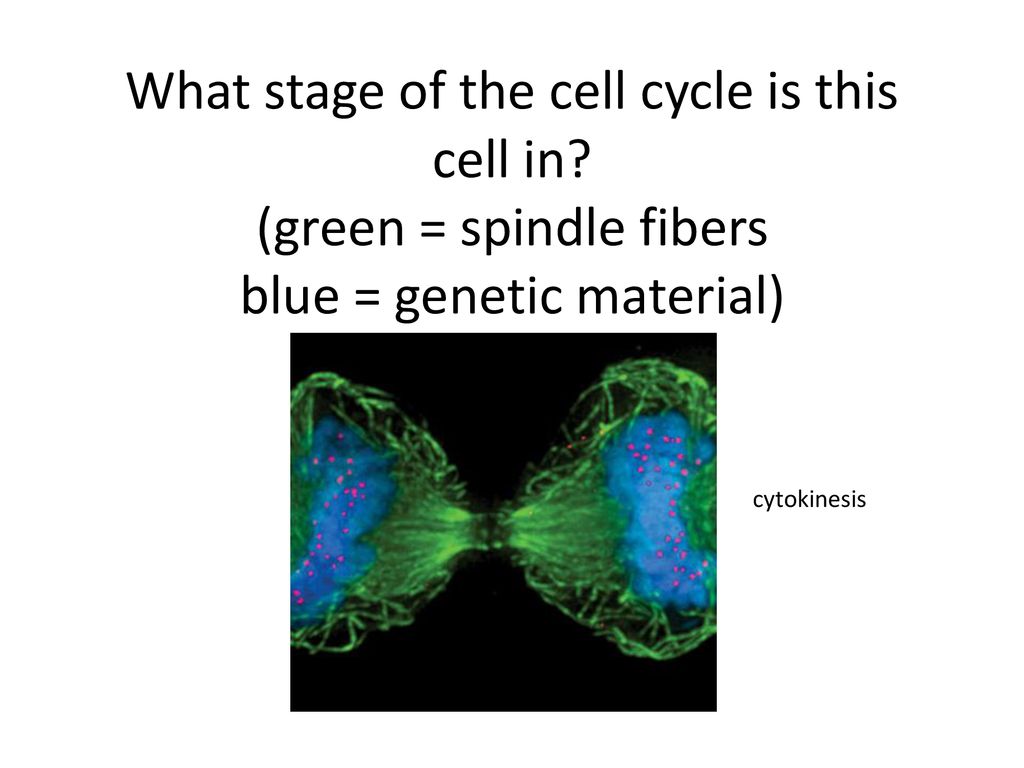
Cell Division Biology Diagrams Learn about the steps and regulation of the cell cycle, a series of events that cells go through to grow, replicate, and divide. The cell cycle has two main phases: interphase and mitosis, each with distinct sub-phases and checkpoints. Learn about the cell cycle, the sequence of events that results in cell growth and division. Explore the phases, regulation, and checkpoints of the cell cycle with diagrams and examples.
Life cycle of the cell Onion cells in different phases of the cell cycle.Growth in an 'organism' is carefully controlled by regulating the cell cycle. Cell cycle in Deinococcus radiodurans. The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell
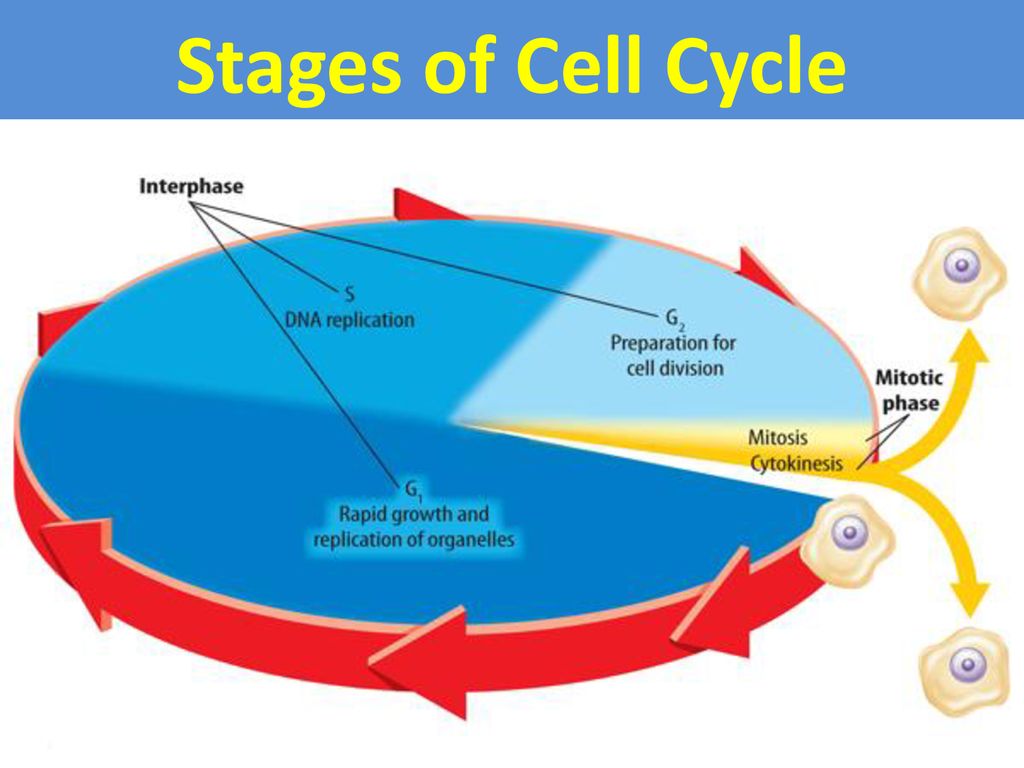
6.2: The Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams
The first stages of the cell cycle involve cell growth, then synthesis close synthesis Made or put together. of DNA close DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid. The material inside the nucleus of cells, Learn about the cell cycle, a cycle of stages that cells pass through to divide and produce new cells. The cell cycle consists of mitosis and interphase, which are divided into sub-phases such as G 1, S, and G 2.

Learn about the phases of the cell cycle, including interphase and mitosis, in this Khan Academy article.

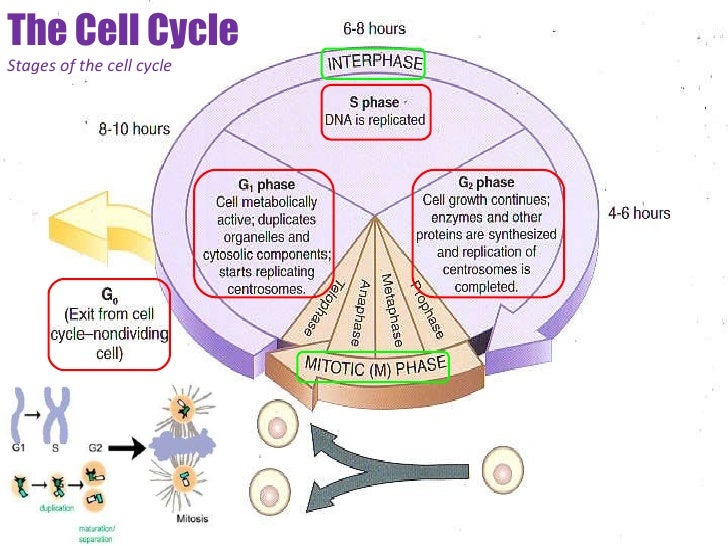
Definition And Phases of Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams
Learn about the cell cycle, the sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides to produce new cells. Find out the phases of the cell cycle, the regulation of cell cycle, and the role of cell cycle in cancer.
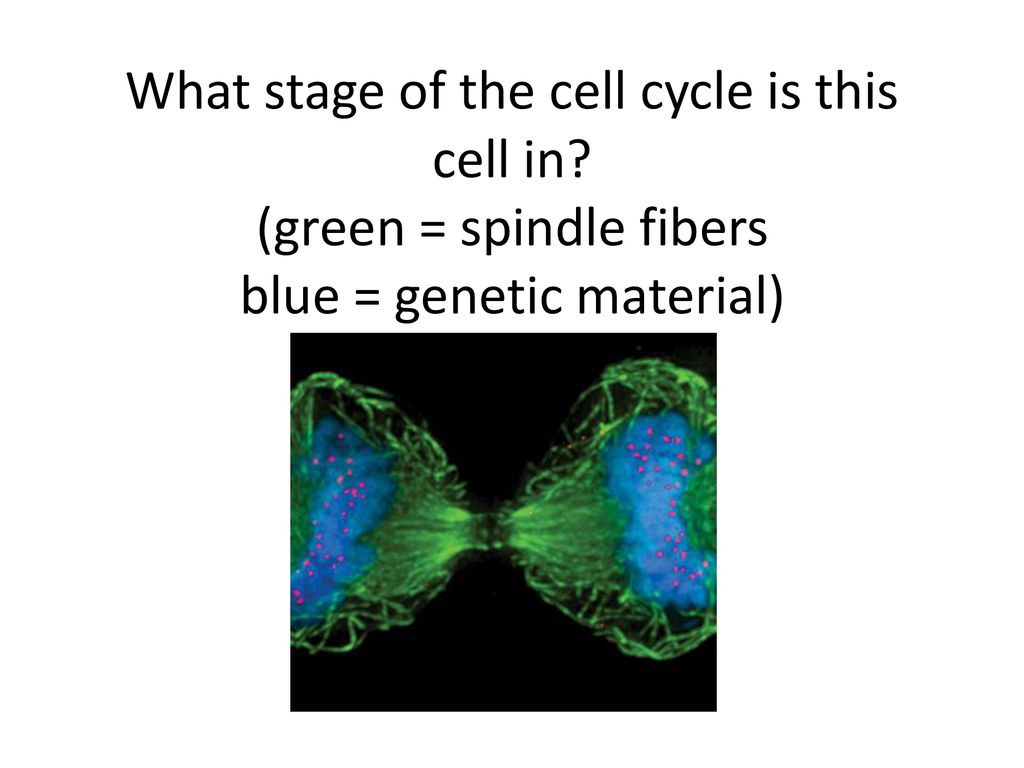
Learn about the ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. The cell cycle has two major phases: interphase and the mitotic phase, each with distinct stages and functions. Learn about the four stages of the cell cycle, the process of cell division, and the differences between mitosis and meiosis. Explore the roles of proteins, checkpoints, and DNA in regulating the cell cycle and preventing cancer.