Cell cycle and Mutation Biology Diagrams Interphase is the phase in the eukaryotic cell cycle during which the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division, In summation, while interphase serves as a preparatory phase for cell division, its manifestation and significance vary across different cell types. From non-dividing specialized cells to rapidly renewing During interphase, the cell grows, duplicates its DNA, and synthesizes proteins and organelles necessary for the next division. The stages of interphase encompass G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase, each contributing vital processes to cellular preparation. The Importance of Interphase in the Cell Cycle. The significance of interphase cannot be

Interphase and the cell cycle. The interphase prepares the cell for the subsequent phases in cell division such as mitosis and cytokinesis. Since interphase is a preparation phase for the cell division processes, it enables the cell to grow, synthesizing organelles that allow the cell to function adequately ones it matures.
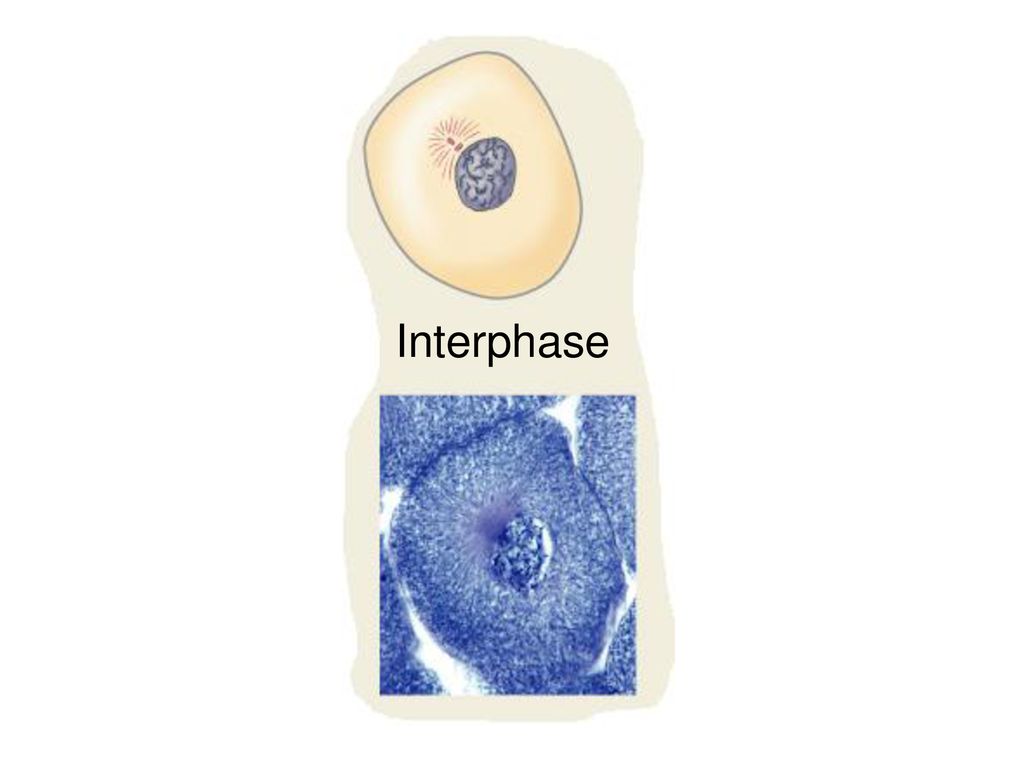
Difference Between Interphase and Prophase Biology Diagrams
Before a dividing cell enters mitosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. About 90% of a cell's time in the normal cell cycle may be spent in interphase. G1 phase: The period before the synthesis of DNA. In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. The G1 phase is the first gap phase. However, the interphase is equally important, We will explore the different stages of interphase, the cell's complex processes that take place within it, and its significance in the functioning of biological organisms. Figure 1: Different phases of the cell cycle in human cells are majorly studied under 2 headings; interphase and cell Understanding interphase is vital for grasping how cells divide and function properly. This article delves into the stages of interphase and their significance in cellular processes. The Cell Cycle Overview. The cell cycle consists of two main phases: interphase and the mitotic phase (M phase). Interphase includes three stages: G1, S, and G2.

Significance of Interphase. After the completion of interphase, the cell enters the nuclear division period. The nuclear division can be either mitosis or meiosis.The nuclear division is followed by cytokinesis, which is the cytoplasmic division, forming two daughter cells.These two daughter cells, which are resulted from the mitotic division again enter the G 1 phase. Interphase Definition. Interphase is the longest stage in the eukaryote cell cycle. During interphase, the cell acquires nutrients, creates and uses proteins and other molecules, and starts the process of cell division by replicating the DNA. Interphase is divided into three distinct stages, Gap 1, Synthesis, and Gap 2, which are discussed
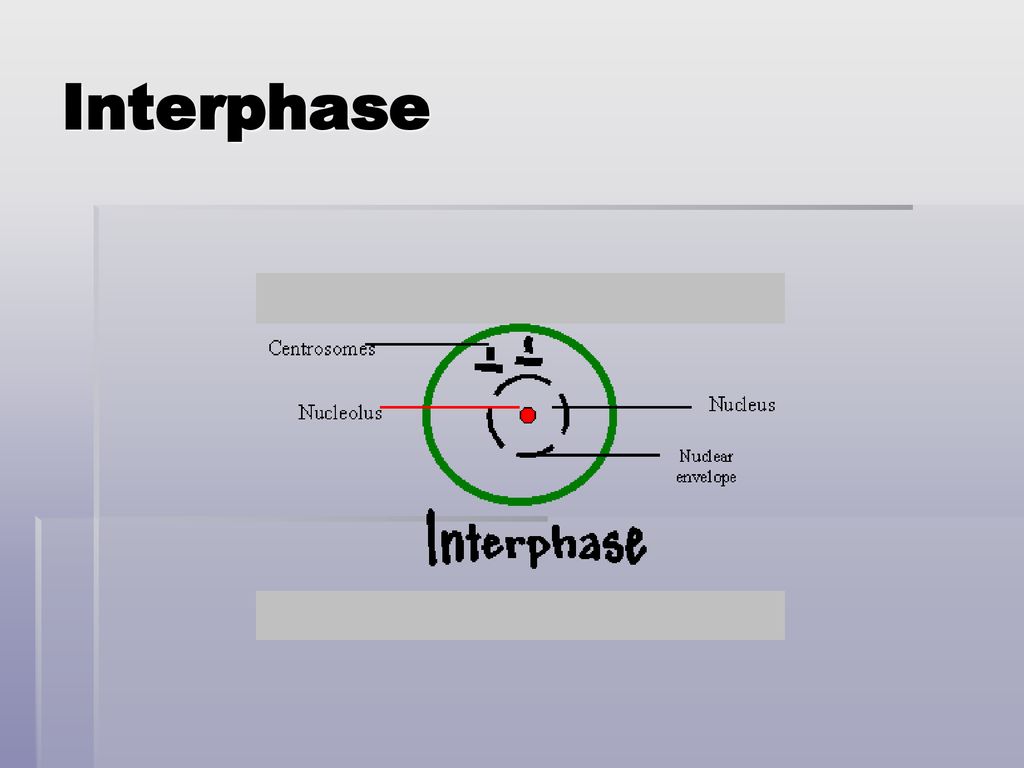
Interphase Biology Diagrams
Interphase is the active portion of the cell cycle that includes the G1, S, and G2 phases, where the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for mitosis, respectively. Interphase was formerly called the " resting phase ," but the cell in interphase is not simply dormant . Moreover, most of the life of a cell is spent in interphase. Students can learn more about the interphase and its various stages here. Interphase Definition and Meaning. Interphase refers to the phase of the cell cycle in which a cell copies its DNA to prepare for mitosis. This phase is also referred to as the 'daily living' or the
