Biophysical Regulation of Histone Acetylation in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Biology Diagrams histone acetylation is regulated through mitosis is only poorly understood. Based on the retention of some acetyl-histone epitopes through mitosis and indirect evidence for ongoing acetylation in mitotic cells (44), Jeppesen (45) and Turner (46) have proposed that HATs remain stably bound to chromosomes Since acetylation is maintained during mitosis, progeny cells receive an imprint of the histone H4 acetylation pattern that was present on the parental chromosomes before cell division. Histone acetylation could provide a mechanism for propagating cell memory, defined as the maintenance of committed states of gene expression through cell lineages.

Long-lasting effects on cellular histone acetylation levels after removal of MS-275 also suggest tight binding to the enzymes Serrano L, Sternglanz R, Reinberg D 2006. SirT2 is a histone deacetylase with preference for histone H4 Lys 16 during mitosis. Genes Dev 20: 1256-1261 [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Ng
Translational Modifications in the Formation ... Biology Diagrams
In this review, we focus on the role of histone PTMs in mitosis, from chromosome condensation to the regulation and activity of the centromere and kinetochore. Arsenic treatment decreases the overall levels of histone acetylation [105,106,107] and H4K16ac by binding to and inhibiting hMOF (the histone acetylase enzyme responsible for the

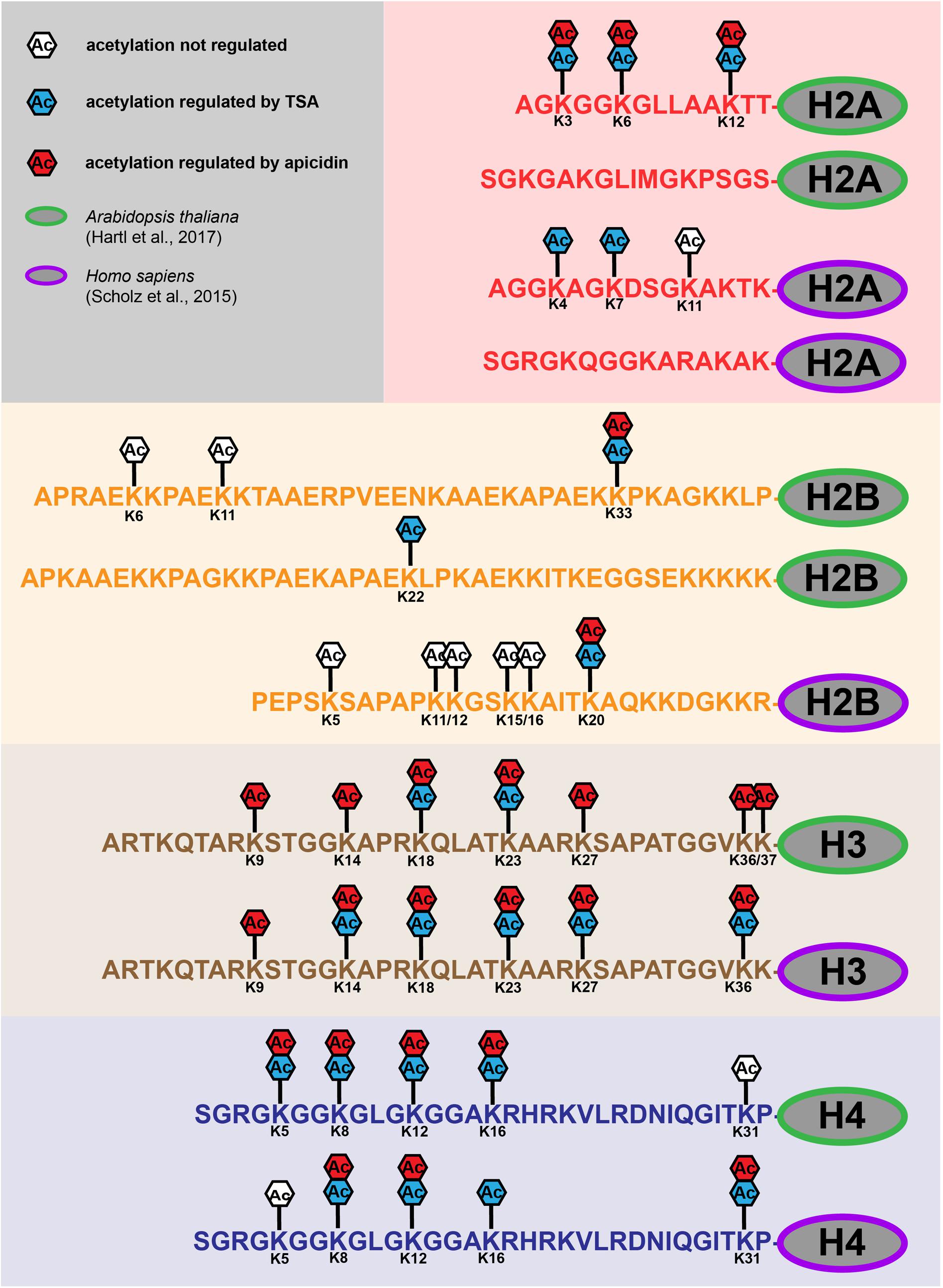
Histone Acetylation and H3 (Lys-4) Methylation at Active and Inducible Genes during Mitosis—It is possible that the maintenance of acetylation and methylation at active promoters serves to signal the reassembly of transcriptional machinery at the G 1 or S phase; in such a case the promoter histone posttranslational modifications could play a Because MS and western blots cannot assess potential changes in the genomic distributions of histone modifications during mitosis, we performed ChIP-seq on either interphase or mitotic differentiating G1E-ER4 cells for total H3, for the mitosis-specific PTM H3S10ph, for four histone acetylation PTMs (H3K14ac, H3K27ac, H3K122ac, and H4K16ac Histone acetylation, a reversible modification of the core histones, is widely accepted to be involved in remodeling chromatin organization for genetic reprogramming. Regulation of global acetylation in mitosis through loss of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases from chromatin J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 12;276(41):38307-19. doi: 10.1074

Regulation of Global Acetylation in Mitosis through Loss of Histone ... Biology Diagrams
Lys 9 H3 acetylation decreases reactivity to the anti-Ser 10 phospho H3 antibody on immunocytochemical preparations. (A) Immunofluorescence detection of Ser 10 phospho H3 histone in different mitotic phases in MRC-5 cells treated for 7 h with 500 ng/ml TSA (+TSA) or receiving 0.1% DMSO (-TSA). Histone acetylation, a reversible modification of the core histones, is widely accepted to be involved in remodeling chromatin organization for genetic reprogramming. Histone acetylation is a dynamic process that is regulated by two classes of enzymes, the histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs). Although promoter-specific acetylation and deacetylation has received
