Arteries anatomy Anatomy and physiology Biology Diagrams At any time, nearly 70% of the total volume of blood in the human body is in the veins. [3] The anatomy of the veins of the heart is very variable, but generally it is formed by the following veins: heart veins that go into the coronary sinus: the great cardiac vein, Anatomy and Physiology. Understanding the Veins: A Detailed Guide to Human Venous System. Explore the intricate human venous system, detailing its structure, function, and the vital role veins play in circulatory health. The inferior vena cava is the largest vein in the human body, transporting blood from the lower half of the body back to

Internal thoracic veins: Superior epigastric veins, Musculophrenic veins, and Anterior intercostal veins are the internal thoracic veins.Supreme intercostal vein Azygos Vein: The azygos vein is a major vein on the right side of the body that drains blood from the posterior thoracic wall and empties into the Superior vena cava. Trunk Veins of the trunk converge from the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis towards the heart. Deoxygenated blood from the thorax ultimately drains into the superior vena cava (SVC).The major thoracic tributaries of the SVC include the: azygos venous system, pulmonary veins, internal thoracic vein and cardiac veins. Venous blood from the abdomen and pelvis is drained by the inferior vena cava.
/vascular-system-veins-56c87fa03df78cfb378b3e7c.jpg)
Veins: Anatomy and Function Biology Diagrams
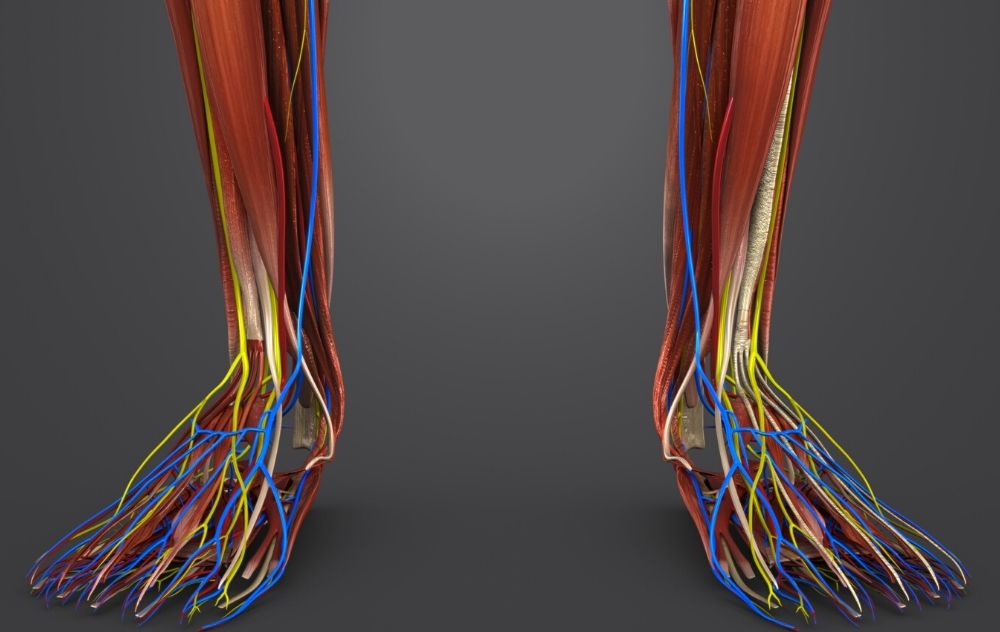
These veins can be found in your muscles and along your bones. Your deep veins do the important work of moving your oxygen-poor blood back to your heart. In your legs, your deep veins hold about 90% of the blood that travels back to your heart. Your deep veins contain one-way valves that keep your blood moving in the right direction. Arterie & vein do vital task of keeping your body healthy and functioning. 862.251.7111. Facebook; Instagram; YouTube; Understanding the makeup of our circulatory system and the anatomy of a vein is an essential part of staying healthy. The largest artery in the human body is the aorta which is attached to the left ventricle of the

Human Vascular System. Veins (blue) and Arteries (red). SEBASTIAN KAULITZK/Science Photo Library/Getty Images. Veins can be categorized into four main types: pulmonary, systemic, superficial, and deep veins. Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.; Systemic veins return oxygen-depleted blood from the rest of the body to the right atrium of the heart. Structure of Veins. Veins are thin-walled valves containing blood vessels. Anatomically, veins have the same three layered walls as arteries that are the tunica externa, the tunica media, and the tunica intima; however, they have considerably lesser amounts of smooth muscles making them thinner than the walls of the arteries. This thinner wall makes the veins more flexible and allows the veins