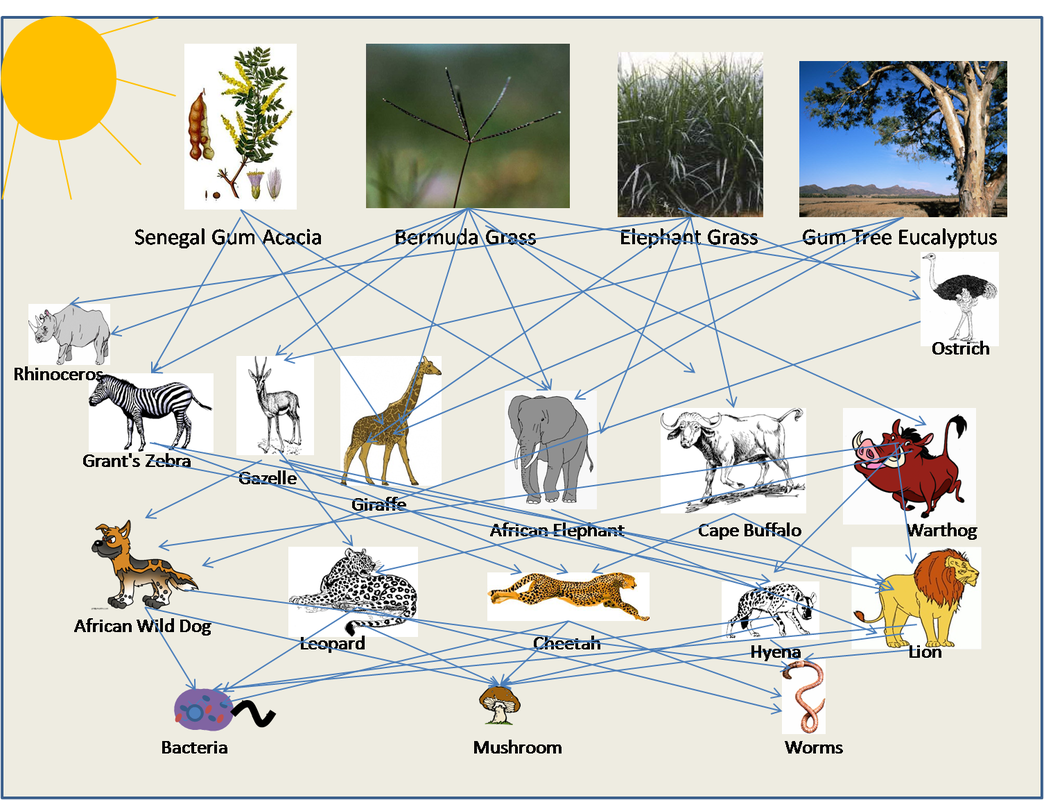
African Savanna Food Chain Diagram Biology Diagrams Termites Act As A Source Of Food . Termites are a popular food item for a range of different animal species. The savanna is home to specialist termite feeders such as the aardvark which consumes huge numbers of termites in one sitting. This insectivorous animal uses its long sticky tongue to penetrate inside termite mounds and fish out the This is an African Savanna Food Web.See if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. Look for: The Producers - the trees, shrubs and grass.. The Primary Consumers - the zebras and elephants.. The Secondary Consumers - the cheetah, hyena.. The Scavengers - the termites, vultures and hyena.. The Decomposers or Detritivores - mushrooms

Food Chain The producers in this biome are; Star grass, red oat grass and Acadia trees. The primary consumers are, grasshoppers, harvester ants, topi, termites, warthogs, dung beetles, hares, mice, impalas, gazelles, and wildebeest The secondary consumers in the biome are know as, the Pangolin, Aardvark, and the mongoose. Besides these mammals, various bird species such as hornbills and woodpeckers also rely on termites, highlighting the insect's extensive role in the food chain. In savanna habitats, termite populations can be remarkably high, with densities exceeding 400/m² of soil, often surpassing the biomass of mammals in the environment. Termites are hugely important to the ecology of the savanna biome. We've covered some of their roles here before when we talked about termite mounds and when we covered nutrients and nitrogen in the savanna biome.The numbers of termites in savanna habitats can be quite extraordinary: with over 400/m 2 of soil, their biomass can exceed that of mammals in the ecosystem.
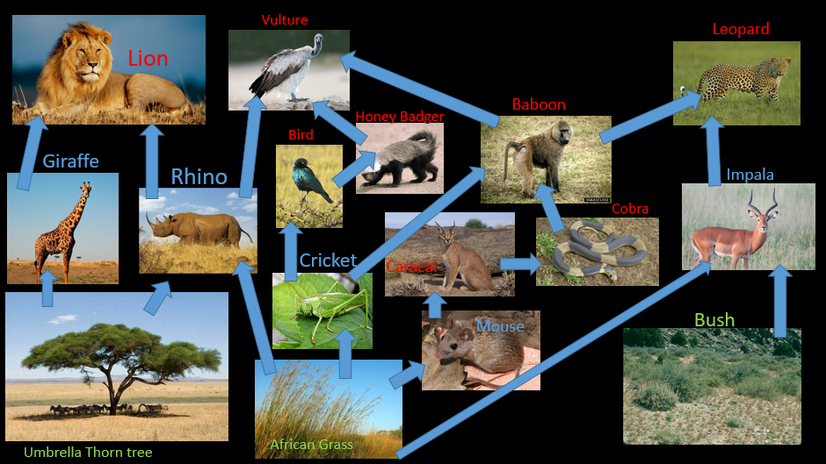
Savanna Decomposers: The Ultimate Termite Guide Biology Diagrams
While wood is a common food source, termites are also omnivorous and will consume fungi, dead plants, and other organic debris, making them detritivores. In the savanna, termites serve as a vital protein source for various tribes, consumed either raw or cooked. Ants, such as red, black, and carpenter ants, actively seek out termite colonies Uncover the vital role of savanna decomposers, termites, in shaping Africa's ecosystems. Explore how these tiny creatures recycle nutrients, influence soil health, and support the food chain. Discover the fascinating impact of termite decomposers on the vibrant savanna landscapes.
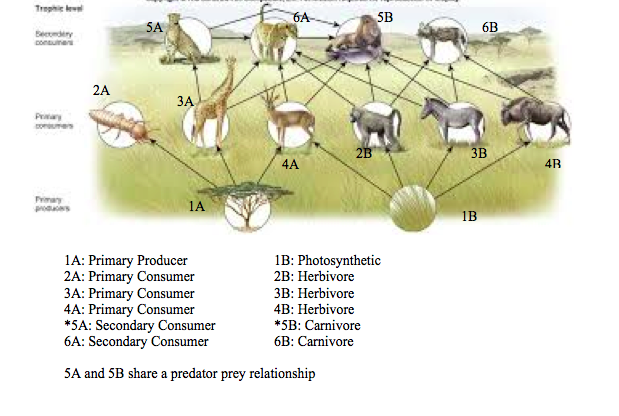
As you move up the food chain, each level receives only about 10% of the energy from the level below it. This energy loss limits most food chains to 3-4 trophic levels. Savanna food chains follow these same principles as energy transfers between trophic levels, beginning with producers. Savanna Food Chain Trophic Levels and Components Explained

Savanna Decomposers Termites Biology Diagrams
The number of termites in savanna habitats can be quite extraordinary, with over 400/m of soil, their biomass exceeding that of mammals. elephants, and giraffes. Additionally, termites are a vital food source for local tribes, offering protein through raw or cooked consumption. Studies demonstrate that the intricate architecture of termite In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of savanna decomposers, focusing on termites. We will explore their fascinating biology, their role as decomposers, and their impact on the savanna environment. By understanding these tiny creatures, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of life that exists in the savanna.