11 questions with answers in MITOTIC INDEX Biology Diagrams For example, skin restores after you cut your finger by cell division (Reece and et al., 2013). To measure a cellular growth or to calculate the percentage of cells in mitosis, researchers use mitotic index value. Mitotic index is the ratio between the amount of cells in a population in the M phase (undergoing mitosis) and the total number of In this image, there is only one cell that is in active division. There are approximately 25 cells total that are visible in the image. For this sample, the Mitotic Index would be calculated as 1 (cells in active division / 25 (total cells) = 0.04. The root tip cells in Figure 1 have a higher Mitotic Index than the cells higher up the root in Determining Mitotic Index Investigating mitosis in root tissue. Growth in plants occurs in specific regions called meristems. The root tip meristem can be used to study mitosis. The root tip meristem can be found just behind the protective root cap. In the root tip meristem, there is a zone of cell division that contains cells undergoing mitosis. Pre-prepared slides of root tips can be studied

Mitosis is a process of nuclear division that involves four distinct stages and forms two genetically identical nuclei It is preceded by interphase, during which the chromosomal DNA is replicated to form sister chromatids Mitotic Index = Cells in mitosis ÷ Total number of cells Calculating Mitotic Index. Index = Mitosis ÷ Total cells 0.

DP IB Biology Revision Notes 2023 - Save My Exams Biology Diagrams
However, in a rapidly dividing cell population, we expect a high proportion of cells to be in the stage of mitosis. One way to quantify cell division is by using the mitotic index: For example, the mitotic index can be used to examine cell proliferation in primary root tissue. The number of cells in mitosis were counted for cells from different The mitotic index is a measure of the proliferation status of a cell population (i.e. the proportion of dividing cells) The mitotic index may be elevated during processes that promote division, such as normal growth or cellular repair. It also functions as an important prognostic tool for predicting the response of cancer cells to chemotherapy The mitotic index is a measure of cellular proliferation. [1]It is defined as the percentage of cells undergoing mitosis in a given population of cells. Mitosis is the division of somatic cells into two daughter cells. Durations of the cell cycle and mitosis vary in different cell types. An elevated mitotic index indicates more cells are dividing.
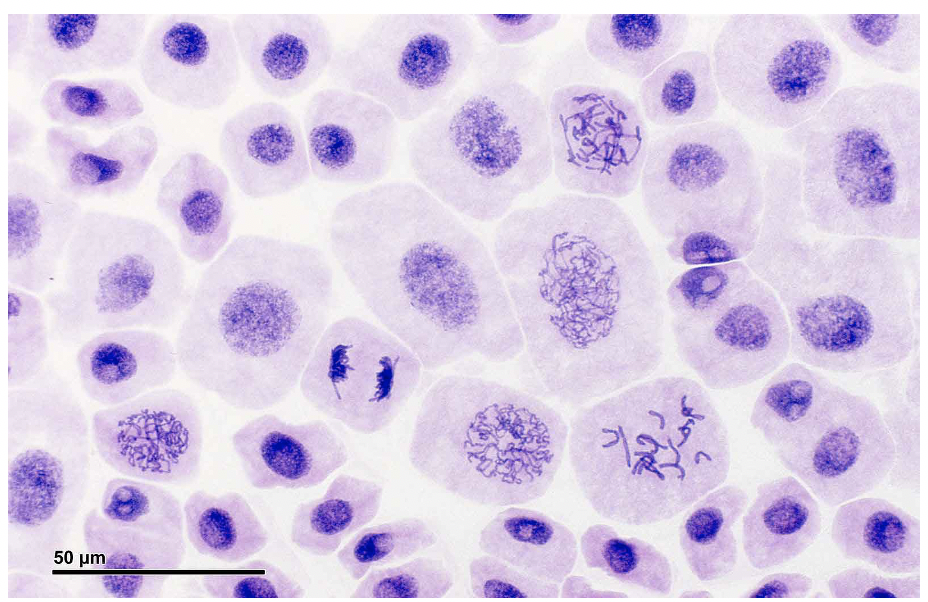
The mitotic index of a cell population is the ratio between the number of cells in mitosis and the total number of cells. It can be used as a clinical tool to determine the degree of cell proliferation within a tissue (e.g. for cancer identification). The mitotic index is calculated using the formula: Aim Mitotic index quantifies the proportion of cells undergoing mitosis within a population. It is calculated by dividing the number of cells in mitosis by the total number of cells in a sample. This index provides insights into cell proliferation, tissue regeneration, and cellular growth. A high mitotic index indicates rapid cell division, while a low index suggests slow or arrested cell growth.
